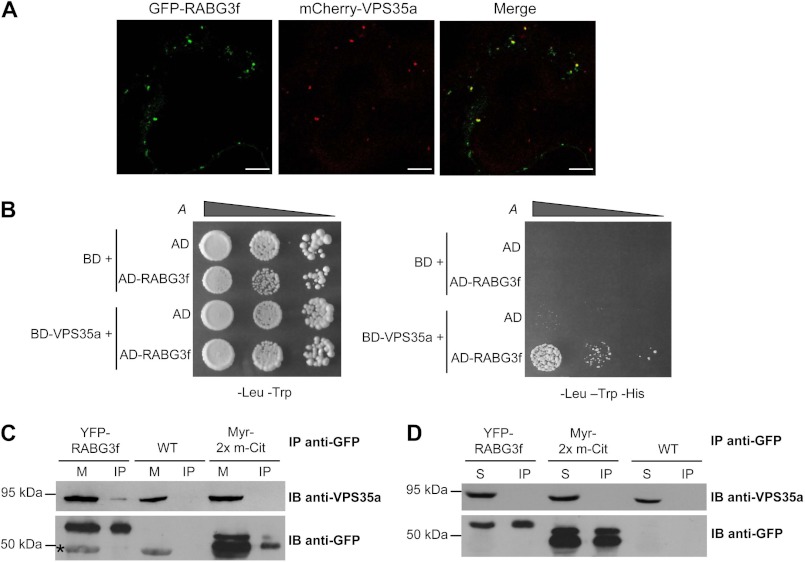
FIGURE 7.
VPS35a associates with RABG3f on membranes. A, co-localization of mCherry-VPS35a with GFP-RABG3f in endosomal compartments. Confocal analysis was performed on epidermal cells of tobacco leaves co-expressing the two fusion proteins. Scale bars, 10 μm. B, yeast two-hybrid test monitoring the interaction between VPS35a and RABG3f. The corresponding empty vectors were used as negative controls. Yeast transformants were grown in liquid cultures and diluted to A600 nm = 0.2, 0.02, and 0.002 and then spotted on −Leu −Trp (left panel) and −Leu −Trp −His (right panel) synthetic complete (SC) medium. The interaction is revealed by the activation of HIS3 transcription and growth on −His medium. AD, Gal4 activation domain; BD, Gal4 DNA binding domain. C, co-IP of YFP-RABG3f and VPS35a with an anti-GFP antibody from microsomal protein extracts of transgenic plantlets expressing YFP-RABG3f. Transgenic plantlets expressing the partially membrane localized protein 2× mCitrine containing a myristoylation tail (Myr-2× m-Cit), as well as wild-type (WT) plantlets were used to test the specificity of the YFP-RABG3f/VPS35a interaction. VPS35a and GFP-tagged proteins were detected with anti-VPS35a and anti-GFP antibodies, respectively. The asterisk indicates a protein that is nonspecifically recognized by the anti-GFP antibody in microsomal fraction. M, microsomal pellet (Input); IP, immunoprecipitate; IB, immunoblotting. D, immunoprecipitation (IP) assays from cytosolic fractions of YFP-RABG3f and Myr-2× m-Cit transgenic and WT plants reveal that VPS35a does not interact with YFP-RABG3f in the soluble fraction. IP and immunodetection were conducted as in C. S, soluble fractions (Input).