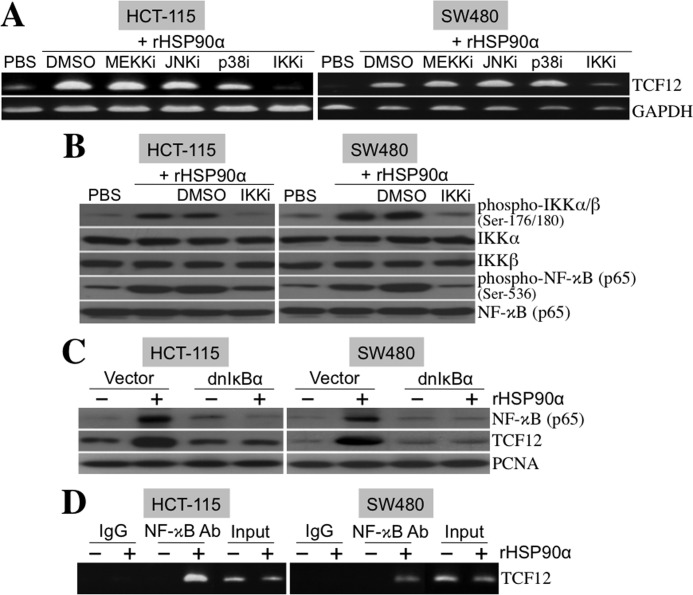
FIGURE 8.
rHSP90α induces cellular TCF12 expression through the NF-κB-dependent pathway. A, RT-PCR was performed to investigate TCF12 mRNA levels in HCT-115 and SW480 cells treated for 24 h with 15 μg/ml rHSP90α in the presence of inhibitors of MEKK (MEKKi; PD98059, 5 μm), JNK (JNKi; SP600125, 5 μm), p38 MAPK (p38i; SB202190, 5 μm), and IKKα/β (IKKi; 6-amino-4-(4-phenoxyphenylethylamino)quinazoline, 0.1 μm). Representative results from three independent experiments are shown. The data indicate that the IKKα/β inhibitor, but not the others, can drastically abolish rHSP90α-induced TCF12 mRNA expression. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide. B, immunoblot analyses of the phosphorylation status of IKKα/β and NF-κB in HCT-115 and SW480 cells treated for 24 h with rHSP90α in the absence or presence of the IKKα/β inhibitor. Representative results from three independent experiments are shown. The data confirm that the IKKα/β inhibitor indeed repressed rHSP90α-induced IKKα/β and NF-κB phosphorylation. C, HCT-115 and SW480 cells were transfected for 48 h with a control vector or dnIκBα-overexpressing plasmid (pRc/CMV-IκB72). Transfected cells were harvested and further treated with PBS or 15 μg/ml rHSP90α for another 24 h. Nuclear extracts were prepared for immunoblot analyses of NF-κB and TCF12 levels. The results show that dnIκBα was efficient in inhibiting rHSP90α-induced nuclear levels of NF-κB and TCF12, confirming that NF-κB is involved in rHSP90α-induced TCF12 expression. The levels of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) were used as internal controls. D, the ChIP assay was performed to indicate a physical association of NF-κB with the TCF12 gene promoter in HCT-115 and SW480 cells treated with 15 μg/ml rHSP90α for 24 h. Representative results from three independent experiments are shown.