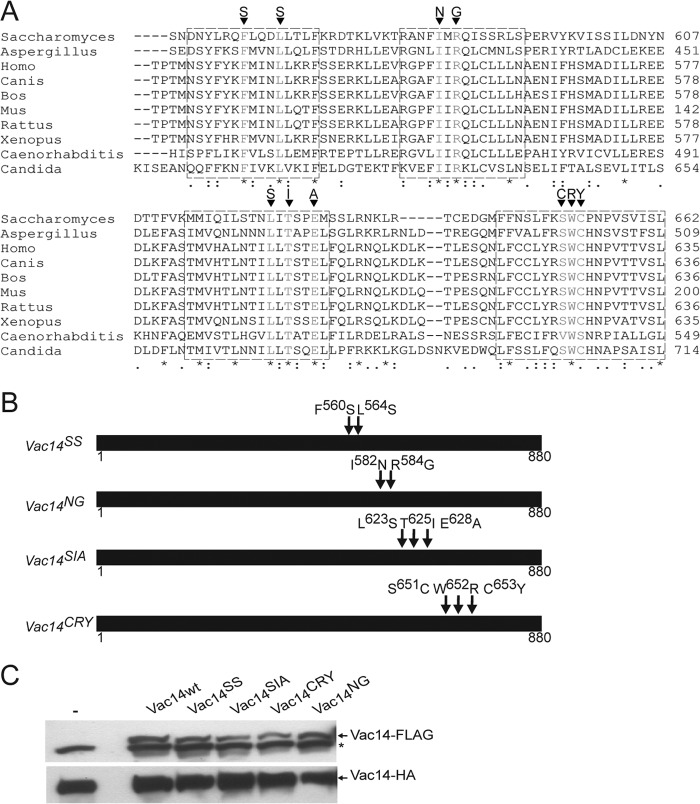
FIGURE 2.
Identification of conserved Vac14 C-terminal motifs. A, sequence alignment of yeast Vac14 and various eukaryotic orthologs using the ClustalW algorithm. * indicates fully conserved residues, a colon indicates strong conservation between groups of similar properties, and a period indicates partial residue conservation. Boxed regions represent selected conserved motifs for site-directed mutagenesis. The targeted mutations are shown for each motif. B, schematic representation of Vac14 point mutants. Arrows show the relative positions of the point mutations in Vac14. C, whole cell lysates from cells genomically expressing Vac14-HA alone (−) or co-expressing FLAG-tagged wild-type Vac14 (Vac14wt) or Vac14 point mutants, were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. Monoclonal anti-FLAG and monoclonal anti-HA antibodies were used to, respectively, detect the FLAG-tagged (top) and HA-tagged (bottom) Vac14 proteins. An * (asterisk) indicates a nonspecific band detected by the anti-FLAG antibody in whole cell lysates.