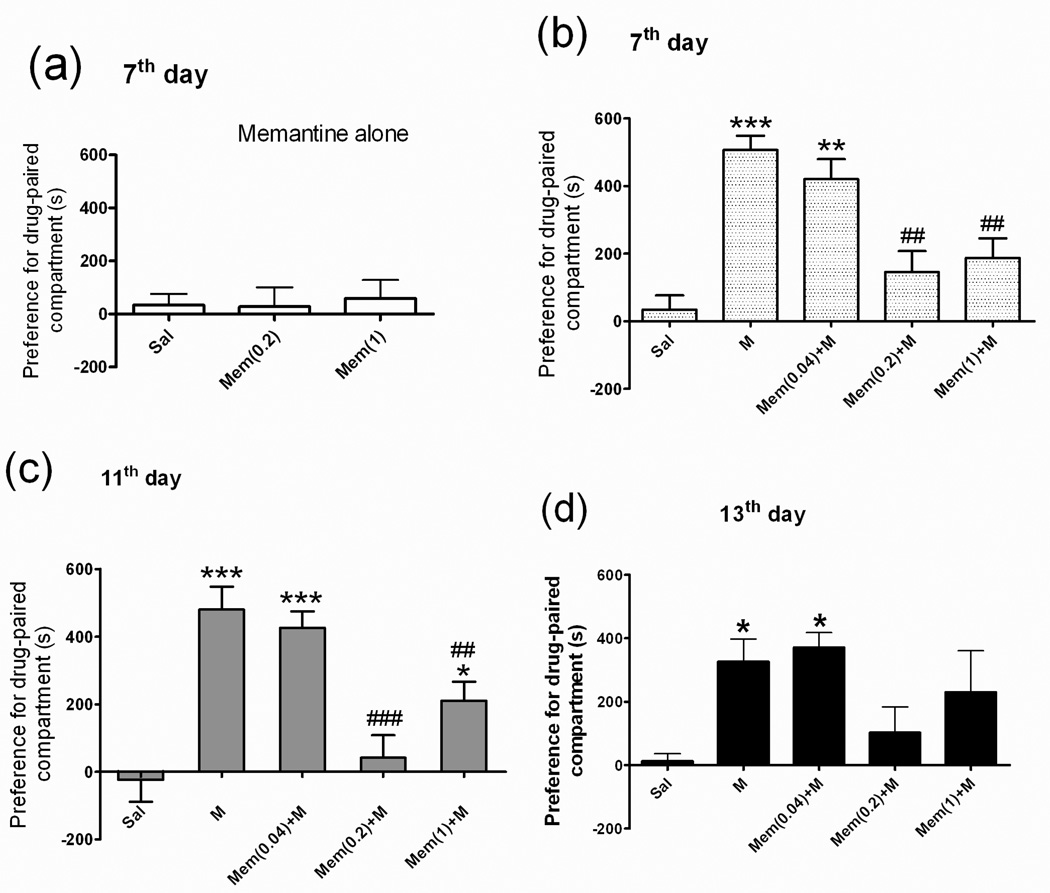
Fig 2. Place preference behavior in rats.
The rats were divided into 7 groups (n = 7–14 each): the saline (Sal) group was given a daily intraperitoneal injection of saline only; the two memantine (Mem) groups were given either a daily subcutaneous injection of 0.2 or 1.0 mg/kg of memantine only; the morphine (M) group a daily intraperitoneal injection of 5 mg/kg of morphine only; the three Mem+M groups were given a daily subcutaneous injection of Mem (0.04, 0.2, or 1.0 mg/kg) plus a daily intraperitoneal injection of 5 mg/kg of morphine. After 6 days of these treatments, the rats were placed in a conditioned place preference (CPP) box for the drug-paired condition. CPP tests were done on days 7, 11, and 13. CPP data (a) for Sal and Mem-only (0.2 or 1) groups on day 7; (b) for Sal, M-only, and Mem+M groups on day 7; (c) for Sal, M-only, and Mem+M groups on day 11; and (d) for Sal, M-only, and Mem+M groups on day 13. Data are means ± S.E.M. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. Sal group. ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. M group (one-way ANOVA).