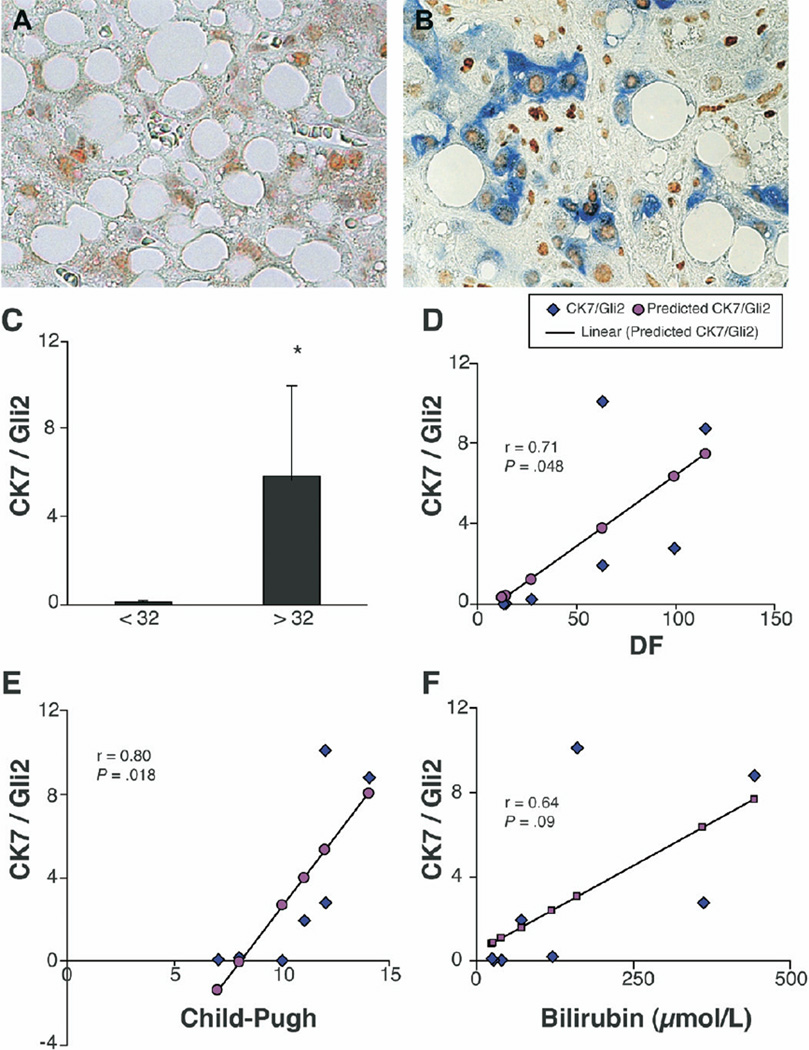
Figure 7.
Lobular accumulation of Gli2/CK7-double positive ductular cells in alcoholic steatohepatitis patients correlates with high short-term mortality risk. Double immunohistochemical staining with Gli2 (brown) and CK7 (blue) in liver parenchyma of representative patient at low risk for short-term mortality (Maddrey discriminant function (DF) <32) (A) and another representative patient with high short-term mortality risk (Maddrey DF >32) (B) (original magnification, ×63). Double (+) cells were quantified by morphometry in 6 parenchymal areas/section in all subjects, and mean ± SD results were compared in patients with Maddrey DF <32 (n = 5) vs Maddrey DF >32 (n = 4) (C). *P < .05. Correlations between accumulation of Gli2/CK7(+) cells and DF (D, P < .05), Child-Pugh score (E, P < .05), and serum bilirubin (F = 0.64) (P < .1).