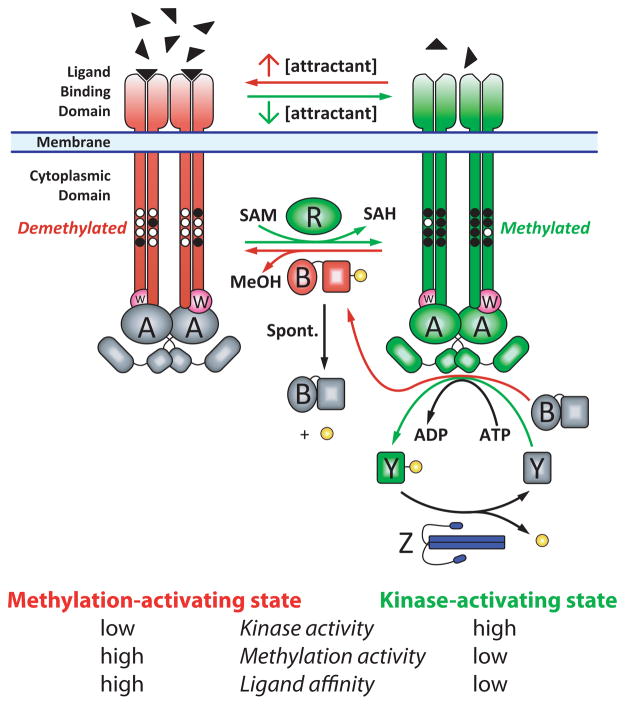
Figure 1.
The E. coli chemotaxis pathway depicted as a two state signaling system. Receptor/CheW/CheA complexes are shown in kinase-stimulating (green/magenta/green) and kinase-inhibiting (red/magenta/gray) states. The binding of attractant (filled triangles) inhibits the CheA kinase (gray A dimer) and stimulates the receptor methylation (black circles) via CheR (green R). Methylated receptors stimulate CheA (green A dimer). The two substrates of CheA, CheY (Y) and the methylesterase (B), are activated by phosphorylation (yellow). CheY-phosphate (green Y) propagates the tumble signal and CheB-phosphate (red B) provides negative feedback by demethylating (and deactivating) receptors. CheB dephosphorylates spontaneously. CheZ (blue Z dimer) dephosphorylates CheY-phosphate. Two features not represented in the figure are the packing of receptor dimers into hexagonal arrays with CheA and CheW, and the unknown receptor:CheA:CheW stoichiometry.