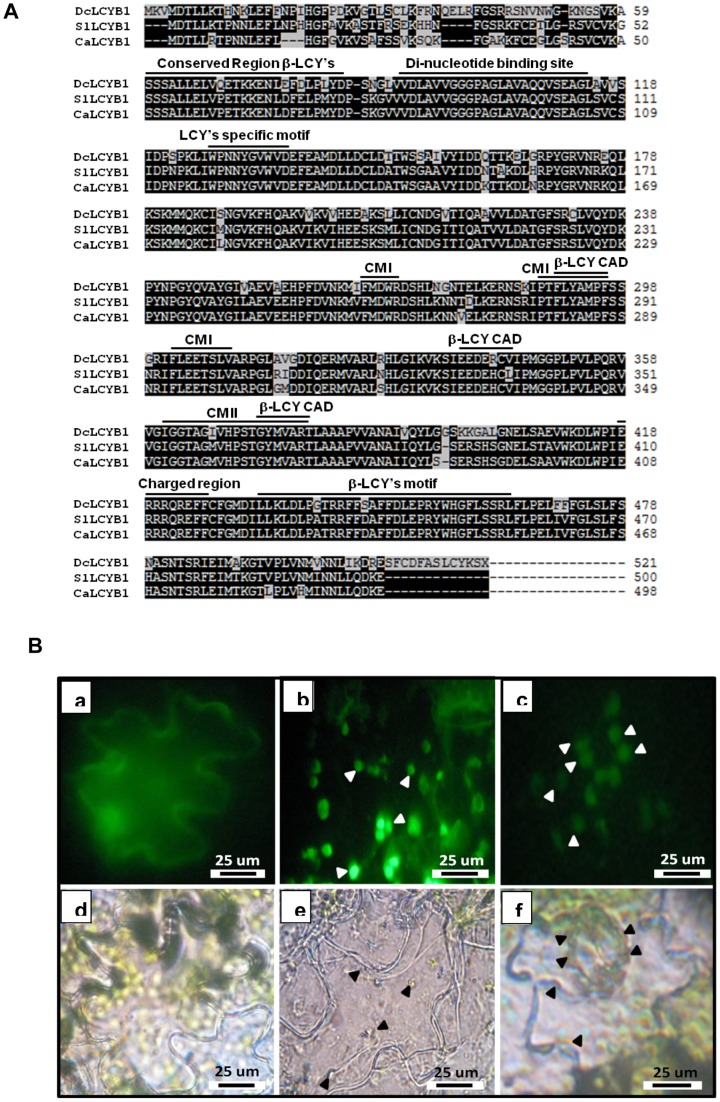
Figure 2. Comparative alignment and sub-cellular localization of DcLCYB1.
(A) The alignment was created using ClustalW. Numbers on the right denote the number of amino acid residues. The amino acid residues which are identical in all sequences are shown in white text on a black background, whereas different residues are shown in black text on a white background. Characteristic regions of plant β-LCYs are indicated above the DcLCYB1 sequence: Conserved β-LCY region, Di-nucleotide binding site, Cyclase motifs (CM) I and II, Charged region and β-LCY motif. Domains described as essential for β-LCY activity are shown as β-LCY CAD (Catalytic Activity Domain). A plant LCY specific motif is also highlighted. SlLCYB1: Solanum lycopersicum lycopene β-cyclase 1; CaLCYB1: Capsicum annuum lycopene β-cyclase 1. (B) Subcellular localization of DcLCYB1. Leaves of two-month old tobacco plants were agroinfiltrated with A. tumefaciens carrying (a) pCAMBIA 35S::GFP, (b) pMDC85-LCYB1 and (c) recA::YFP (positive control). After 4 days, epidermal peels were observed by epi-fluorescence microscope. (a) pCAMBIA 35S::GFP – a cytoplasmic localization of soluble GFP is visible. (b) pMDC85-LCYB1 - the punctuate fluorescence is indicative of a chloroplastic localization of DcLCYB1-GFP. (c) pBI-recA- the punctuate fluorescence is indicative of a chloroplastic localization of recA::YFP. (d, e, f) Bright field images of a, b, c, respectively. All images were taken with 40x augmentation and fluorescence was observed after excitation at 489 nm.