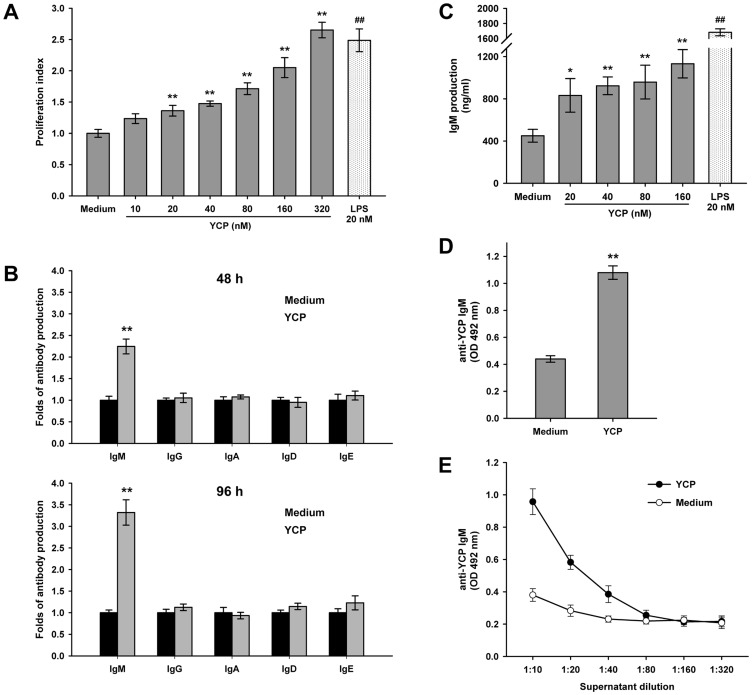
Figure 1. YCP promotes B cell proliferation and induces IgM response.
A: Effect of YCP on B cell proliferation. Splenic B cells were treated with YCP or LPS at the indicated concentrations, and cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay at 48 h (n = 6, ** p≤0.01 vs. medium by Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn's post-hoc test, ## p≤0.01 vs. medium by Mann–Whitney U test). B: The production of IgM, IgG, IgA, IgD and IgE in response to YCP stimulation. Splenic B cells were incubated with 80 nM of YCP for 48 h or 96 h, and supernatants were then collected for quantification of each Ig isotype using sandwich ELISA (n = 5, ** p≤0.01 vs. medium by Mann–Whitney U test). C: A dose-dependent induction of IgM antibodies by YCP at 48 h (n = 6, * p≤0.05, ** p≤0.01 vs. medium by Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn's post-hoc test, ## p≤0.01 vs. medium by Mann–Whitney U test). D: IgM reactivity to YCP in supernatants from naïve and YCP-treated B cells. Splenic B cells were left untreated or treated with YCP for 48 h, and the supernatants collected from each group were subjected to measurement of YCP-bound IgM using indirect ELISA (n = 6, ** p≤0.01 vs. medium by Mann–Whitney U test). E: Titration of IgM antibodies to YCP in supernatants from naïve and YCP-stimulated B cells (n = 6, ** p≤0.01 vs. medium by Mann–Whitney U test).