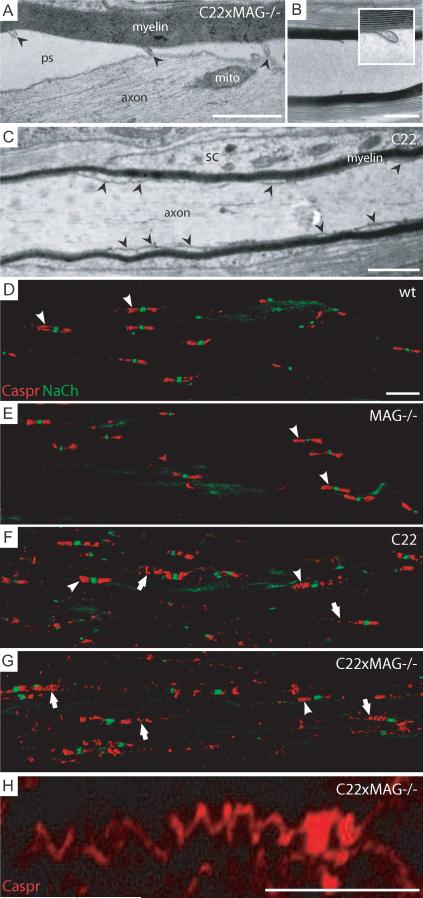
Figure 6. Ectopically localized loops of the lateral rim in C22 and MAG-deficient C22 mice.
Ectopically localized loops of the cytoplasmic rim of the myelin membrane were observed within the internodal region (A, arrowheads; B inset; pictures were taken from animals at P40 as example). These ectopically, normally paranodally localized, loops were often still attached to the axonal membrane, although the inner mesaxon of the internode lost axonal contact (A). In some longitudinal sections they were still present even if no axon was visible (B). In C22 animals, similar phenomenon was observed, showing ectopically localized loops of the lateral rim within the internode (C, arrowheads). Immunofluorescent staining for Caspr revealed a distended spiral structure of its localization over more than 20μm (G; higher magnification, H), which was never observed in wildtype (D) and MAG-deficient mice (E). In C22 animals normal (F, arrowheads), but also distended Caspr localization could be observed, although not to such an extend as in double mutant mice (F, arrows). Pictures were taken from animals at P48 as example. Scale bars: (A–C) 1 μm; (D–G and H) 10 μm. Abbreviations: ps, periaxonal space; mito, mitochondria, sc, Schwann cell cytoplasm.