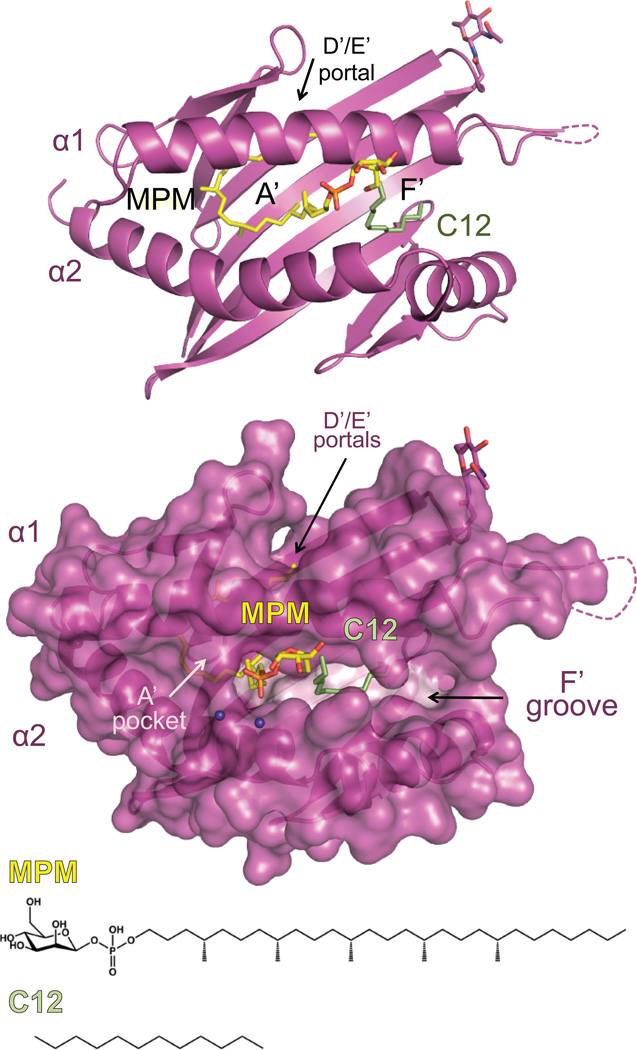
Figure.
The structure of the Group 1 CD1 molecule, CD1c, is shown in magenta in ribbon (top) and surface (bottom). CD1c is presenting the mycobacterial lipid derived from M. tuberculosis, mannosyl-β1-phosphomycoketide (MPM), shown in yellow. Apparent in the structure was also a C12 spacer hydrocarbon chain, shown in pale green. The chemical structures of these lipids are shown at the bottom. CD1c has the canonical A’ and F’ pockets, however CD1c has a modified structure, including a unique exit portal (D/E portal) and an open F’ pocket resembling a groove-like structure. These modifications allow CD1c to present a unique repertoire of lipid antigens such as mycoketides and lipopeptides.