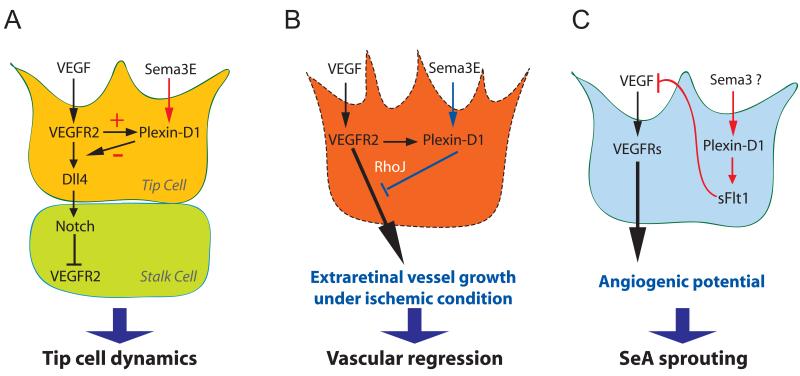
Fig. 2. Sema3E-Plexin-D1 signaling in regulating vascular patterning via its interaction with VEGF signaling.
(A) Tip cell dynamics are regulated by Sema3E-Plexin-D1 modulating Dll4-Notch signaling via a VEGF-induced negative feedback mechanism [15]. VEGF directly controls the expression of Plexin-D1 selectively in endothelial cells at the front of actively sprouting blood vessels. In turn, Sema3E-Plexin-D1 signaling inhibits the activity of VEGF-induced Dll4-Notch signaling pathway, which controls the balance between tip and stalk cells, thereby the retinal vascular network topology.
(B) Sema3E-Plexin-D1 signaling contributes to proper vasculature formation after pathological condition such as ischemic retinopathy [16]. Sema3E-Plexin-D1 signaling counteracts VEGF-mediated signaling and the small GTPase RhoJ might be involved in modulating the two pathways. Under the ischemic retinopathy condition, abnormal extraretinal vascular projections are suppressed by enhancing Sema3E-Plexin-D1 signaling. (C) Plexin-D1 signaling induces soluble flt-1 expression to negatively control VEGF signaling in zebra fish truck [17]. During zebrafish segmental artery development, Plexin-D1-mediated signaling limits aorta’s angiogenic potential by inhibiting VEGF signaling via soluble flt-1. The specific member of Sema3 subfamily that mediates this event in the zebrafish is yet to be identified.