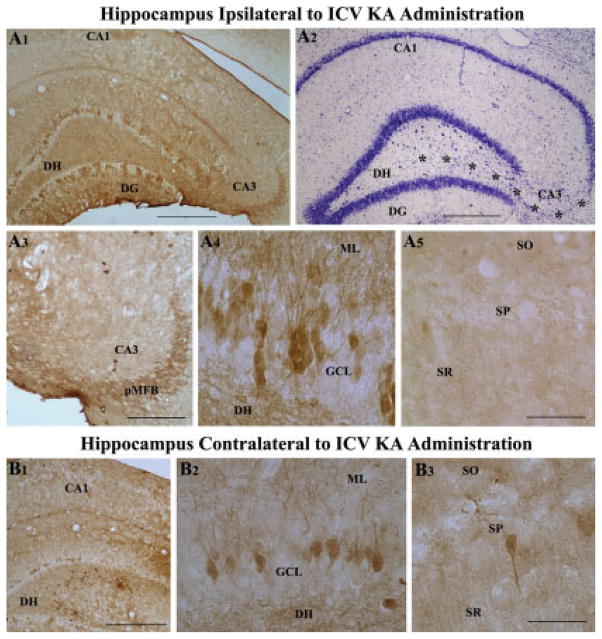
FIGURE 4.
Bilateral loss of hippocampal calbindin immunoreactivity following unilateral intracerebroventricular kainic acid (ICV KA), visualized at 6 months post-administration (A1–B3). A1 is an example of hippocampus ipsilateral to ICV KA demonstrating severe loss of calbindin in dentate granule cells and CA1 pyramidal neurons. Nissl-stained adjacent section however shows intact cell layers in the dentate gyrus and the CA1 subfield (A2). A3–A5 are magnified views from A1, illustrating diminished calbindin immunoreactivity in the principal mossy fiber bundle (pMFB) located in the CA3 region (A3), loss of calbindin in a major fraction of dentate granules (A4), and virtually all CA1 pyramidal neurons (A5) following KA administration. B1 is an example of hippocampus contralateral to ICV KA demonstrating loss of calbindin in dentate granule cells and CA1 pyramidal neurons. B2 and B3 are magnified views of regions from B1 illustrating loss of calbindin immunoreactivity in the dentate gyrus (B2) and CA1 subfield (B3). DG, dentate gyrus; DH, dentate hilus; SO, pMFB, principal mossy fiber bundle; stratum oriens; SP, stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum. Scale bar: A1, A2, B1 = 500 μm; A3 = 200 μm; A4, A5, B2, B3 = 100 μm.