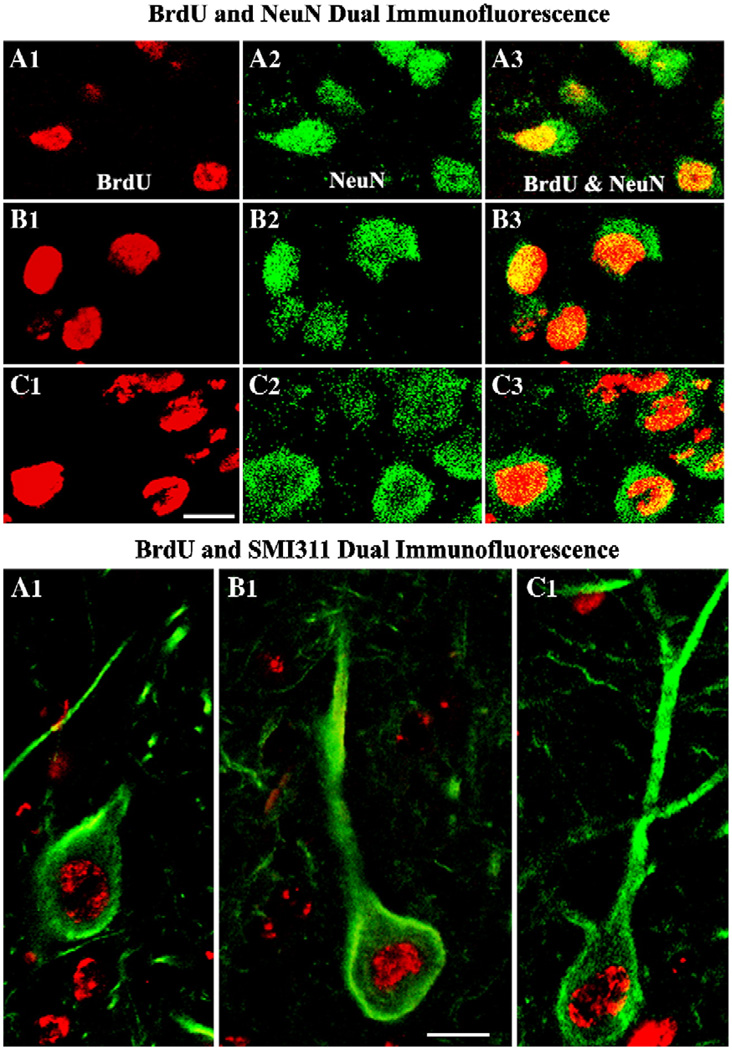
Fig. 5.
Differentiation of grafted cells into neurons (upper panel) and CA3 pyramidal-like neurons (lower panel). The upper panel (A1–C3) illustrates confocal images of grafted neurons that are positive for 5′-bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) and neuron-specific nuclear antigen (NeuN) in standard hippocampal fetal cell (HFC) grafts (A1–A3), HFC grafts treated with BDNF, NT-3 and caspase inhibitor (B1–B3) and HFC grafts treated with FGF-2 and caspase inhibitor (C1–C3). Note that a vast majority of transplanted cells differentiate into NeuN positive neurons in all groups. The lower panel shows representative confocal images of grafted neurons that are positive for BrdU and a CA3 pyramidal neuron marker (the non-phosphorylated neurofilament protein) from standard HFC grafts (A1), HFC grafts treated with BDNF, NT-3 and caspase inhibitor (B1) and HFC grafts treated with FGF-2 and caspase inhibitor (C1). Scale bar, upper panel (A1–C3) = 10 µm; lower panel (A1–C1)=10 µm.