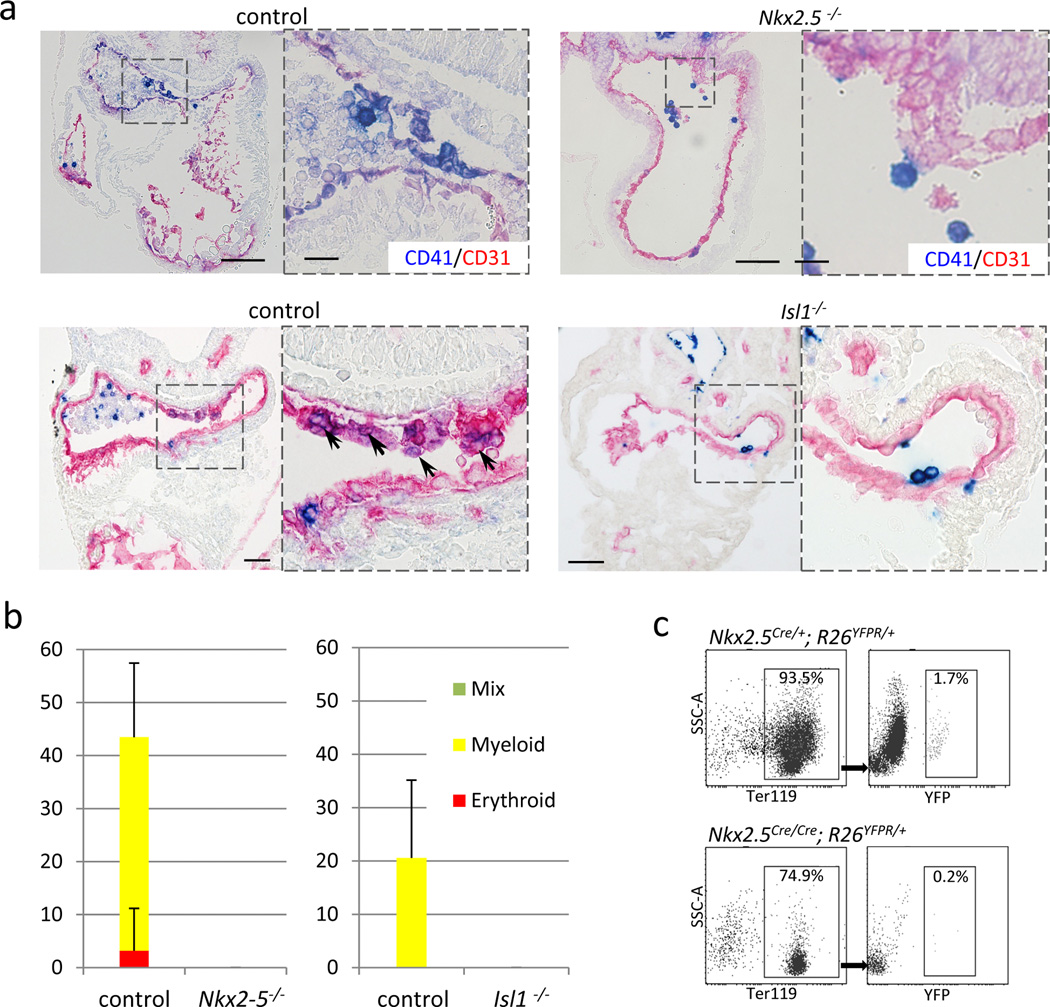
Figure 5. Figure 5. Endocardial hematopoiesis depends on Nkx2-5 and Isl1.
- Nkx2-5 mutant heart at E9.5 stained for CD41 (blue) and CD31 (red). CD41+ cells were hardly found in the endocardium of Nkx2-5 mutants. Note that Nkx2-5 mutant also develops known cardiac defects including a single ventricle with poorly developed trabeculae, open atrioventricular canal, and lack of epithelial-mesenchymal transformation in the endocardial cushion. Scale bar = 100µm.
- Nkx2-5-derived endocardial cells in Nkx2-5 hetero (left panels) and null (right panels) background. Nkx2-5-driving cells were identified in the cushion endocardium even in the absence of Nkx2-5.
- Blood colony formation assay from FACS-purified endocardial cells. No colonies were formed from Nkx2-5 mutant endocardial cells. Data represent average of three independent experiments.
- Comparison of the peripheral blood cells derived from Nkx2-5-expressing cells in Nkx2-5-null and its control backgrounds at E10.0. YFP-labeled red blood cells (Ter119+) were found less frequently (0.2%) in Nkx2-5Cre/Cre; R26YFPR/+ embryos compared with control littermates (1.7%), suggesting that expression of Nkx2-5 is required for the hemogenic activity of the Nkx2.5+ endocardial/endothelial cells in vivo.