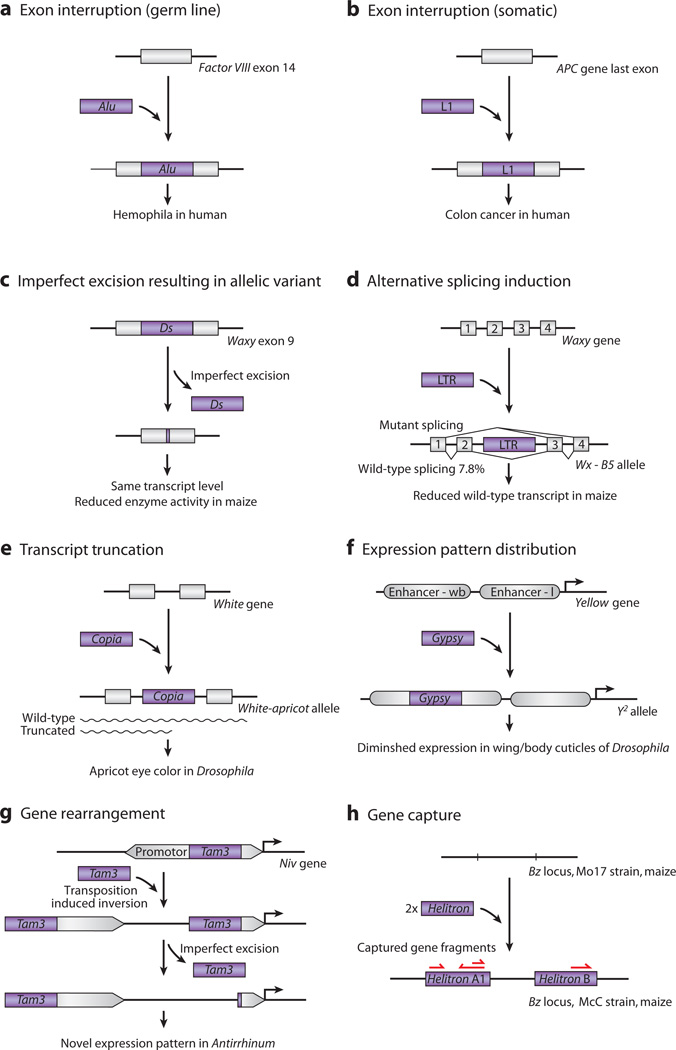
Figure 2.
Functional impact of de novo insertions. (a) Exon interruption (germ line). A heritable human Alu SINE retrotransposon insertion interrupting exon 14 of human factor VIII gene causes hemophilia (117). (b) Exon interruption (somatic). A somatic insertion of a human L1 retrotransposon leads to loss of function of the APC gene, thereby promoting colon cancer development (85). (c) Long terminal repeat (LTR) recombination resulting in allelic variant. Recombination between the two LTRs of a Gret retrotransposon at the VvmybA1 locus rescued its gene expression. This recombined allele, VvmybA1b, reconstituted the expression of skin pigment in red grapes (68). (d) Alternative splicing induction. Insertion of an LTR retrotransposon in the waxy locus leads to exon skipping and kernel color changes in maize due to reduced transcript level (122). (e) Transcript truncation. A copia LTR retrotransposon insertion in Drosophila causes a hypomorphic white allele (white-apricot, w[a]). The intronic insertion causes truncated and nonfunction transcripts, with some read-through transcripts remaining functional; the result is the apricot phenotype (78). (f) Gene silencing. In the Melon genome, a hAT family DNA transposon inserted into the second intron of CmWIP1 gene leads to the spread of DNA methylation to the promoter region and subsequent gene silencing. Organisms with this insertion develop female flowers because of repressed CmWIP1 gene expression (82). (g) Gene rearrangement. A Tam3 DNA transposon–related inversion at the niv locus in Antirrhinum. The inversion results from DNA breaks on opposite ends of replicated copies of Tam3 rather than on opposite ends of a single copy. Their recombination with the upstream sequence leads to an inversion with altered niv promoter sequences and reduced expression. Excision of the proximal Tam3 causes another allele with increased and novel patterning of anthocyanin pigment (21). (h) Gene capture. Helitron DNA transposons inserted at the bronze (bz) locus in maize have also captured several neighboring genes, leading to their duplication and significant noncolinearity at this locus in different strains. Functional consequences have not been shown (124).