Fig. 5.
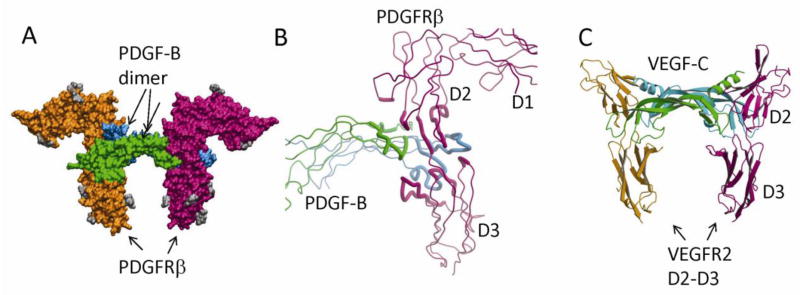
PDGF:PDGFR recognition. (A) The surface model of the PDGF-B in complex with the D1-D3 domains of PDGFRβ. PDGF-B protomers are colored in green and cyan, and PDGFRβ is colored in magenta and orange. The N-linked glycans are colored in gray. (B) The recognition involves the dimeric seam of PDGF-B, extending two arms clamping the D2-D3 boundary of PDGFRβ. Both PDGF-B and PDGFRβ are shown as tubes, and the interacting parts are shown as thicker tubes than the rest. (C) PDGF:PDGFR recognition is reminiscent of VEGF:VEGFR recognition. Shown is the ribbon model of VEGF-C in complex with the D2-D3 domains of VEGFR2. Despite roughly equivalent structural elements involved, there are major differences including the interface chemistry, the domain orientations, and the length of the L1 loops.
