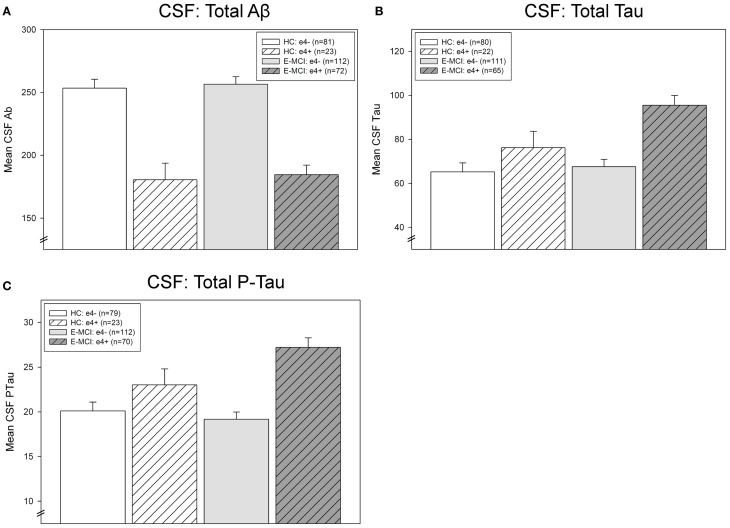
Figure 4.
Effects of APOE ε4 status and diagnosis on CSF protein levels in E-MCI and HC participants. Diagnostic group and APOE ε4 status significantly affected CSF levels of Aβ (A), total tau (B), and p-tau (C). CSF Aβ was significantly associated to APOE ε4 status (p < 0.001), with APOE ε4+ E-MCI and HC participants showing lower levels of Aβ than APOE ε4− E-MCI and HC participants, regardless of diagnosis. Total tau levels were significantly affected by both diagnosis (p < 0.05) and APOE ε4 status (p < 0.001), with E-MCI patients showing higher total tau levels than HC participants and APOE ε4+ showing higher levels than APOE ε4− participants. Finally, an interaction between diagnostic status and APOE ε4 status on CSF p-tau levels was also observed (p < 0.05), primarily driven by a higher level of p-tau in APOE ε4+ HC and E-MCI participants relative to APOE ε4− HC and E-MCI participants. The total number of participants in each analysis is shown for each graph (Panels A–C). Note: See text for description of participants excluded from the CSF analysis.