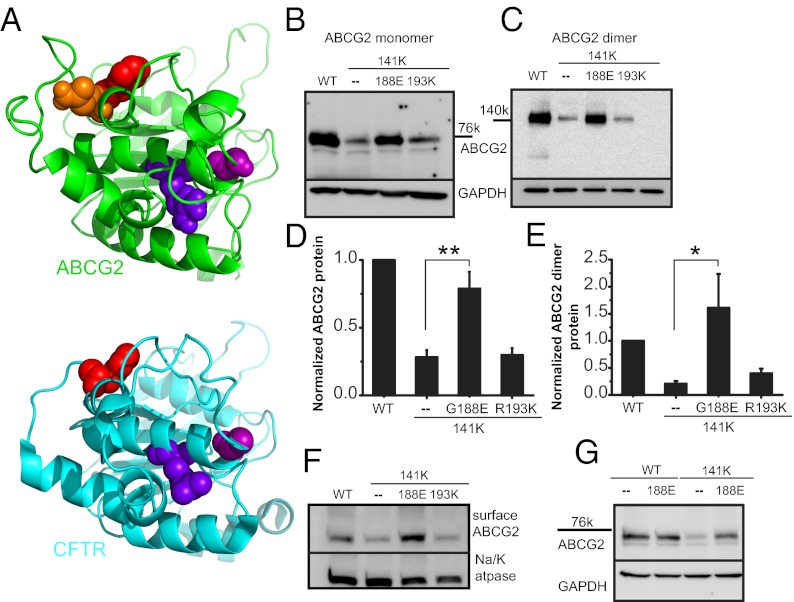
Fig. 3.
Suppressor mutation correction of Q141K expression defect. (A) Structural model of human ABCG2 NBD (green structure) and human CFTR NBD1 (blue structure, PDB ID: 2PZE). The NBD dimer interface is approximately on the right, and the NBD–TMD interface is approximately on the top. The following residues are shown as spheres (ABCG2/CFTR): orange, Q141; red, F142/F508; blue, R193/R555; purple, G188/G550. Western blot of transient total (B) and dimer (C) expression in CHO cells of suppressor mutations in the Q141K background. Summary data of suppressor rescue of Q141K ABCG2 total (D; n = 10) and dimer protein expression (E; n = 4). (F) Surface expression of biotinylated ABCG2 and Q141K variants and Na+/K+ ATPase, demonstrating strong rescue with the Q141K G188E mutation (n = 6). (G) The G188E mutation does not affect WT ABCG2 protein expression (n = 3). All means are ± SEM; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.