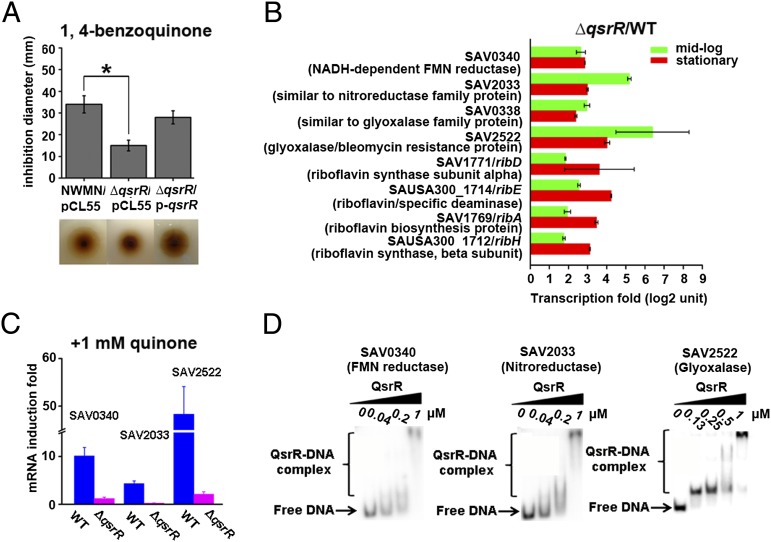
Fig. 1.
QsrR is involved in quinone signaling and response. (A) Disk-diffusion assays showing that QsrR impacts bacterial resistance toward 1,4-benzoquinone. The wild-type strain (NWMN/pCL55), ∆qsrR mutant (∆qsrR/pCL55), and complementation strain (∆qsrR/p-qsrR) were assayed with 2 M 1,4-benzoquinone and incubated overnight before data collection. The experiments were performed in triplicate with consistent results. *P < 0.01 (Student t test). (B) Selected genes differentially expressed in the ∆qsrR mutant compared with the wild-type strain from transcriptomic profiling. Transcriptomic profiling was performed at both of the midlog and stationary growth stages. The experiments were performed in duplicate with consistent results. (C) Quinone stress impacts the expression of QsrR target genes in a QsrR-dependent manner. The mRNA levels of SAV0340 (FMN reductase), SAV2033 (nitroreductase), and SAV2522 (glyoxalase) were monitored before and after treatment of 1 mM 1,4-benzoquinone at midlog growth stage by qRT-PCR. The experiments were performed in triplicate with consistent results. (D) QsrR directly binds to the promoter regions of SAV0340, SAV2033, and SAV2522. EMSAs were performed at a serial concentration of QsrR ranging from 0 to 1 μM with the 32P-labeled DNA.