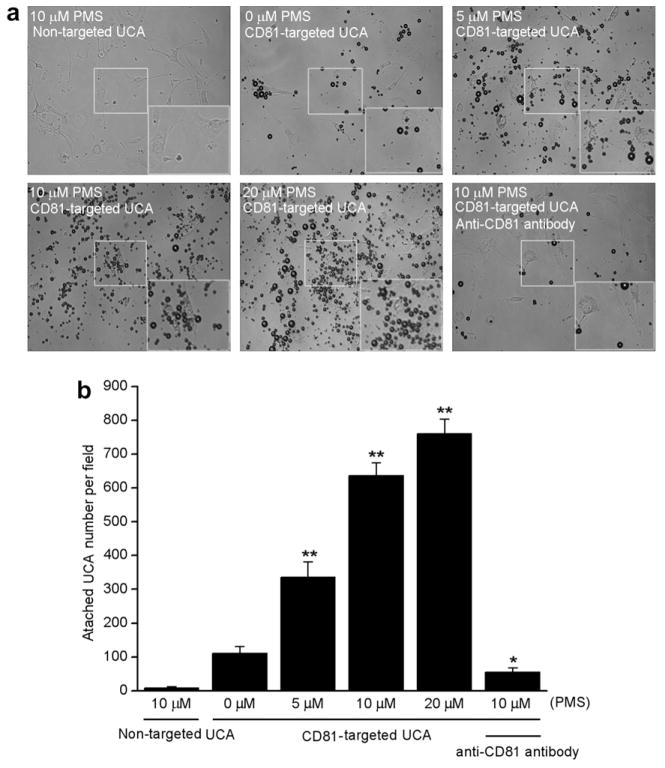
Fig. 3.
CD81-targeted ultrasound contrast agents (UCA) binding to cultured bEnd.3 cells. (a) Representative micrograph for CD81-targeted UCA or non-targeted UCA adhered to cells stimulated with 0, 5, 10 or 20 μM phenazine methosulfate (PMS)(×200). Non-targeted UCA was not able to bind to the cells stimulated with 10 μM PMS (top left). Just a few CD81-targeted UCA was able to bind to the cells without PMS stimulation (top middle). The number of CD81-targeted UCA was gradually improved with increase of PMS concentration from 5 μM (top right), 10 μM (bottom left) to 20 μM (bottom middle). Pre-incubation using 1 μg/mL free anti-CD81 antibodies with 10 μM PMS-stimulated cells inhibited greatly the binding of CD81-targeted UCA to the cells (bottom right). The boxes located the center of pictures stand for the selected regions amplified for making the cells more visible. The boxes located the bottom right of pictures stand for the amplified view of the selected regions. (b) Quantitative assay of the number of UCA adhered onto bEnd.3 cells from six at random view field. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs non-stimulation control (n = 6).