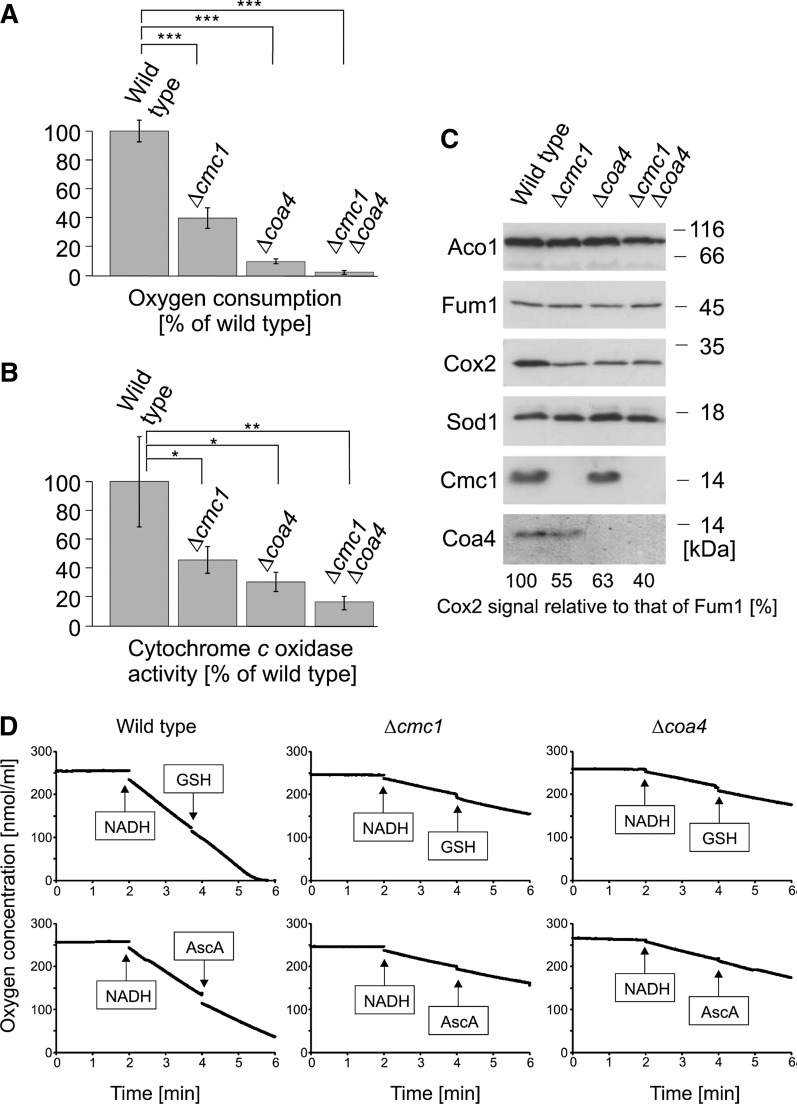
FIG. 5.
Δcmc1 and Δcoa4 mutants show reduced levels of cytochrome c oxidase. (A) Mitochondria (100 μg) isolated from the indicated strains were incubated in 0.6 M sorbitol, 1 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), 1 mM MgCl2, and 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4 in a reaction chamber containing a Clark electrode, and oxygen consumption was measured over time. Mean values and standard deviations of three independent measurements are shown. (B) Activity of cytochrome c oxidase was measured in mitochondrial extracts by following the oxidation of reduced cytochrome c over time. Mean values and standard deviations of three independent measurements are shown. (C) Mitochondrial proteins (100 μg) were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against the indicated proteins. The signals of Cox2 and Fum1 were quantified and the levels of Cox2, corrected for the levels of Fum1, are shown in the figure. (D) The addition of GSH or ascorbic acid (AscA) does not stimulate oxygen consumption of isolated mitochondria. Oxygen concentrations of mitochondria-containing solutions were recorded before and after the addition of NADH, GSH, and AscA. Shown are mean values of two measurements per sample. Asterisks indicate confidence levels as follows: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.