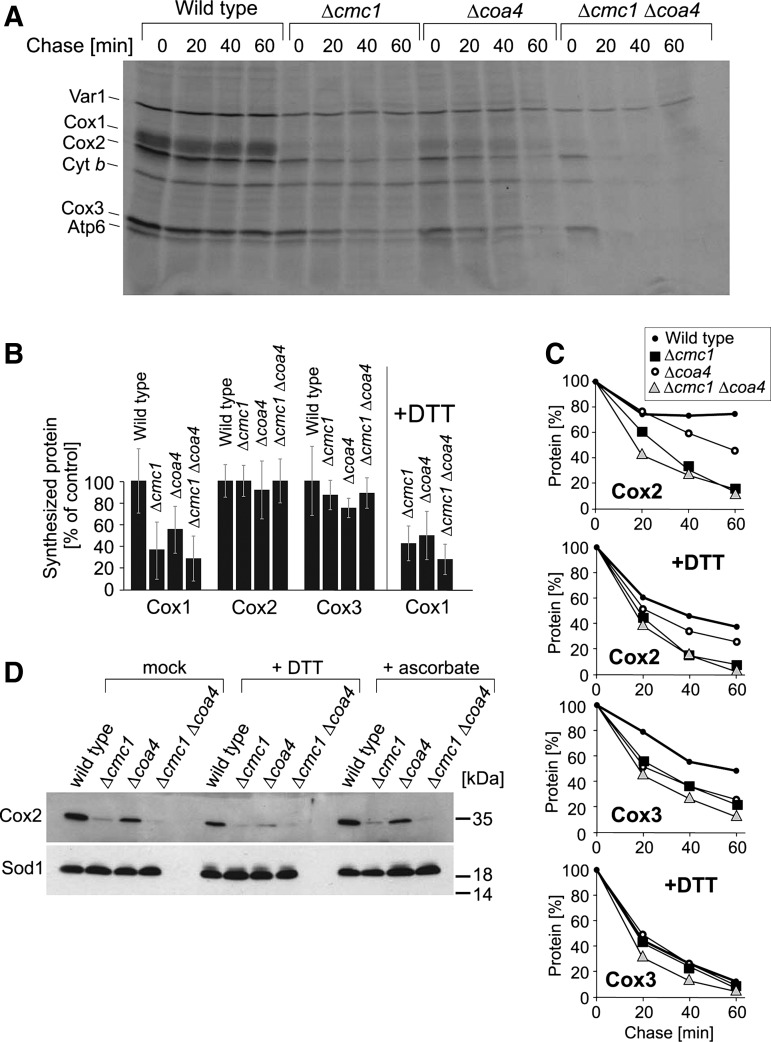
FIG. 6.
The biogenesis of cytochrome c oxidase is impaired in Δcmc1 and Δcoa4 mutants. (A) Mitochondrial translation products were radiolabeled with [35S]-methionine for 15 min in cells after inhibition of cytosolic protein synthesis with cycloheximide. Labeling was stopped by washing of cells and addition of an excess of nonradioactive methionine. Cells were further incubated for the time periods indicated (“chase”), lysed, and analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and autoradiography. (B, C) The experiment shown in (A) was repeated three times in the absence or presence of 1 mM DTT. The levels of newly synthesized Cox1, Cox2, and Cox3 normalized to the levels of the soluble matrix protein Var1 at chase time 0 were quantified (B). In (C), mean values of the intensities of Cox2 and Cox3 signals are shown relative to the values found at chase time 0. (D) Western blot signals of Cox2 and Sod1 of cells grown in the absence or presence of 5 mM DTT or ascorbic acid are shown. It should be noted that the addition of DTT or ascorbic acid did not increase the levels of Cox2 in the mutants.