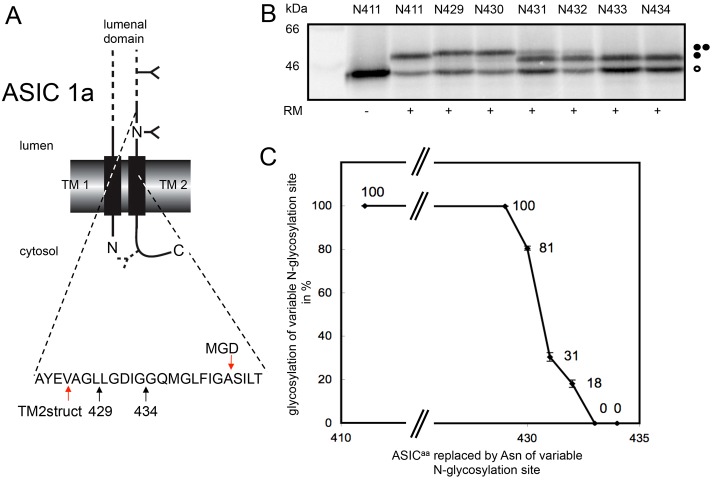
Fig. 4.
Defining the extra-cytoplasmic boundary of ASIC1a-TM2 using MGD mapping. (A) Chicken ASIC1a was engineered to contain two N-glycosylation sites (cf. Fig. 1), one fixed at residue 402 and a second variable site located between residues 411 and 434 as indicated. The location of a third cryptic N-glycosylation site at residue 476 of the cytoplasmic tail is indicated. Arrows labelled 429 and 434 indicate the luminal region of ASIC1a analysed by N-glycosylation scanning (cf. B), whilst the two arrows labelled TM2struct and MGD indicate the extra-cytoplasmic boundary of TM2 as deduced from the crystal structure and minimal glycosylation mapping, respectively. (B,C) The amounts of the variously modified species were quantified and plotted as for P2X2 analysis (see legend to Fig. 1). All symbols are as previously defined in the legend to Fig. 1.