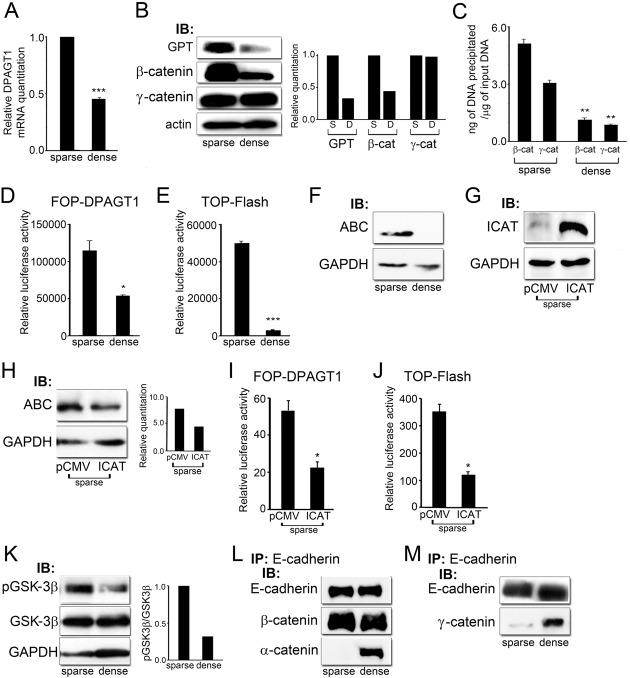
Fig. 1.
DPAGT1 senses cell density via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. (A) Quantitative PCR of DPAGT1 transcript levels in sparse and dense MDCK cells (***P<0.001). (B) Immunoblot of GPT, β-catenin and γ-catenin expression in sparse and dense cultures. Bar graphs: fold change in GPT, β- and γ-catenin levels after normalization to GAPDH. (C) ChIP analyses of β-catenin and γ-catenin at the DPAGT1 promoter in sparse and dense cells after normalization to the IgG control (**P<0.005). (D) Luciferase reporter activity from the FOP-DPAGT1 vector in sparse and dense cells (*P<0.05). (E) Luciferase reporter activity from the TOP-Flash vector in sparse and dense cells (***P<0.001). (F) Immunoblot of ABC expression in sparse and dense cells. (G) Immunoblot of ICAT in sparse cells after transfection with control vector, pCMV, and vector with ICAT under the CMV promoter. (H) Immunoblot of ABC in sparse cells transfected with either the pCMV control vector or vector with ICAT. Bar graph: fold change in ABC levels after normalization to GAPDH. (I) Luciferase reporter activity from the FOP-Flash vector in sparse cells transfected with either the pCMV control vector or ICAT (*P<0.05). (J) Luciferase reporter activity from the TOP-DPAGT1 vector in sparse cells transfected with either the pCMV control vector or ICAT (*P<0.05). (K) Immunoblot of pGSK-3β and GSK-3β expression in sparse and dense cultures. Bar graph: fold change in pGSK3β/GSK3β levels after normalization to GAPDH. (L) E-cadherins were immunoprecipitated from sparse and dense cultures and their association with β-catenin and α-catenin was assessed by immunoblot. (M) E-cadherins were immunoprecipitated from sparse and dense cultures and their association with γ-catenin was assessed by immunoblot.