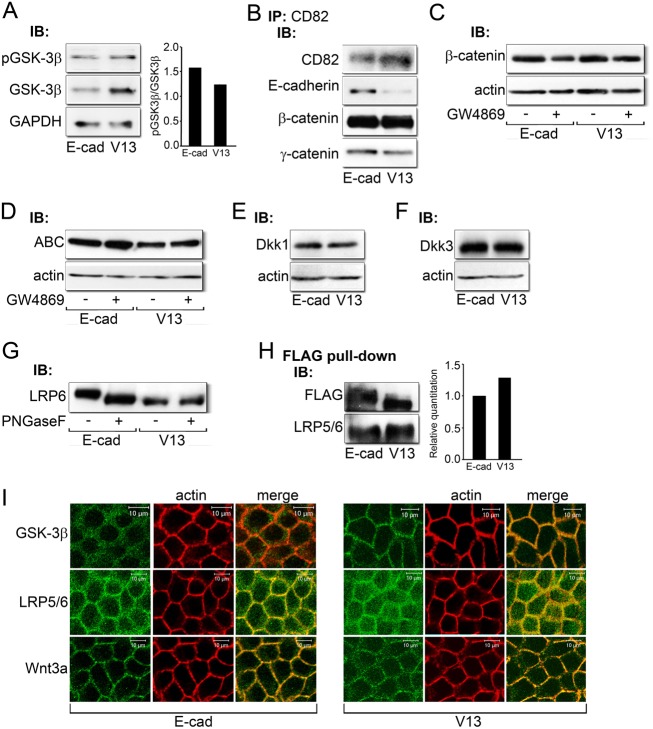
Fig. 6.
Potential mechanism of V13 action. (A) Immunoblot of pGSK-3β and GSK-3β expression in E-cad and V13 cells. Bar graph: fold change in the pGSK-3β/GSK-3β ratio after normalization to GAPDH. (B) Immunoblot of co-immunoprecipitation of CD82 tetraspanins with E-cadherin, β-catenin and γ-catenin from E-cad and V13 cells. (C) Immunoblot of β-catenin expression after inhibition of sphingomyelin synthesis by GW4869 in E-cad and V13 cells. (D) Immunoblot of ABC protein levels after inhibition of sphingomyelin synthesis by GW4869 in E-cad and V13 cells. (E) Immunoblot of Dkk1 protein levels in E-cad and V13 cells. (F) Immunoblot of Dkk3 expression in E-cad and V13 cells. (G) Immunoblot of LRP6 before and after treatment with PNGaseF from E-cad and V13 cells. (H) Immunoblot of FLAG pull-down of E-cadherins from E-cad and V13 cells and their association with LRP5/6. Bar graph: fold change in LRP levels after normalization to FLAG. (I) Immunofluorescence localization of GSK-3β, LRP5/6 and Wnt3a in E-cad and V13 cells counterstained for F-actin. Scale bars, 10 µm.