Fig. 7.
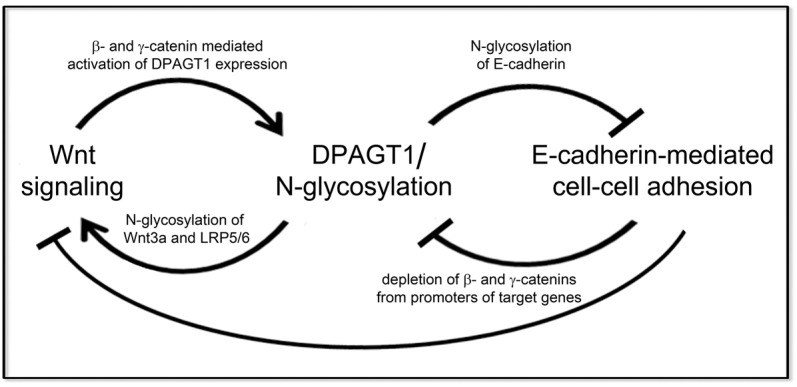
Interactions among canonical Wnt signaling, DPAGT1/N-glycosylation and E-cadherin. Schematic illustrating the positive and negative feedback loops among E-cadherin, canonical Wnt signaling and DPAGT1/N-glycosylation. Canonical Wnt signaling activates DPAGT1 transcription, and DPAGT1 promotes N-glycosylation of Wnt components to further enhance Wnt signaling. High DPAGT1 expression causes extensive N-glycosylation of E-cadherin, which, in turn, inhibits E-cadherin adhesion. Under conditions of diminished canonical Wnt signaling, DPAGT1 expression is reduced, leading to hypoglycosylation of E-cadherin. Hypoglycosylated E-cadherin inhibits canonical Wnt signaling by depleting β- and γ-catenins from promoters of target genes, including the DPAGT1 promoter, thus maintaining low canonical Wnt activity, DPAGT1 expression and the hypoglycosylated status of E-cadherin in mature AJs.
