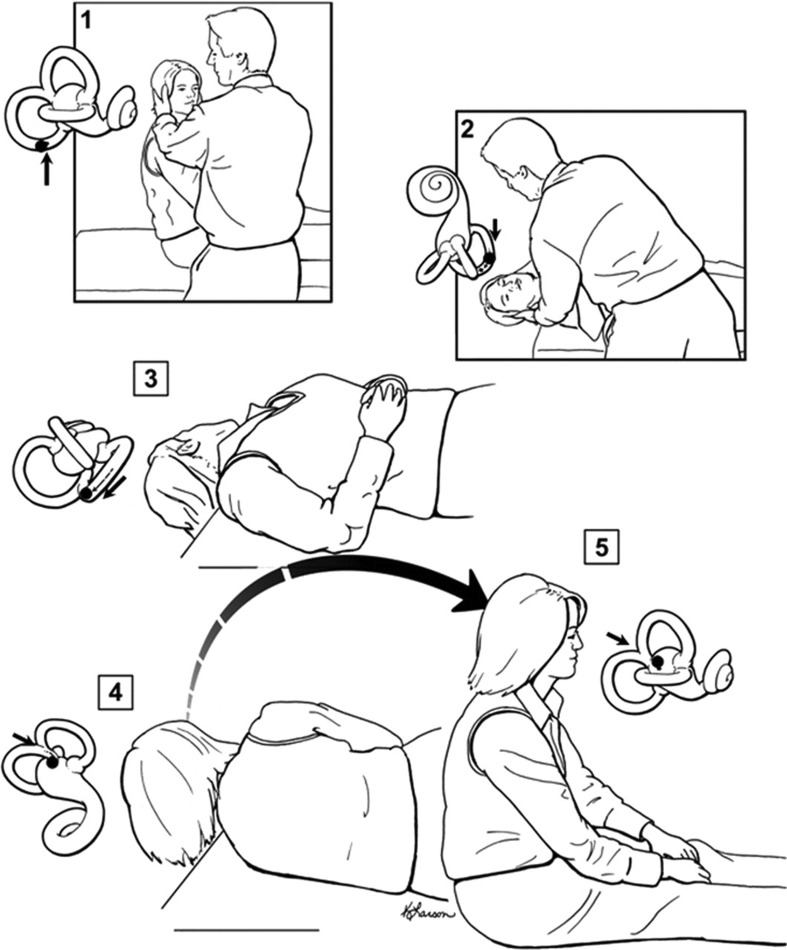
Figure 2. The Dix-Hallpike test and the canalith repositioning maneuver.
The Dix-Hallpike test is performed by turning the patient's head about 45 degrees toward the side to be tested (step 1) and then laying the patient down quickly (step 2). If BPPV is present, nystagmus ensues usually within seconds. The patient is held in the right head-hanging position (step 2) for 20 to 30 seconds, and then the remaining steps of the canalith repositioning maneuver can be performed (steps 3–5). In step 3, the head is turned 90 degrees toward the unaffected side. Step 3 is held for 20 to 30 seconds before turning the head another 90 degrees (step 4) so the head is nearly in the face-down position. Step 4 is held for 20 to 30 seconds, and then the patient is brought quickly back up to the sitting up position. The movement of the otolith material within the labyrinth is depicted with each step, showing how otoliths are moved from the posterior semicircular canal to the vestibule. From: Fife T, Iverson T, Lempert J, et al. Practice parameter: therapies for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology 2008;70:2067–2074.