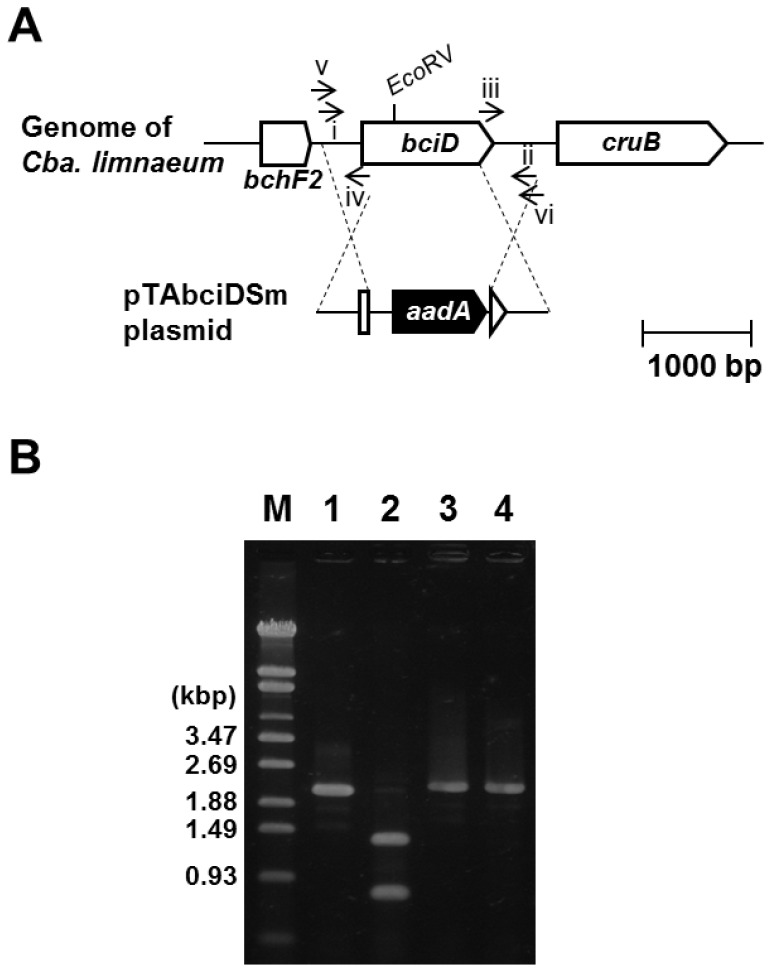
Figure 2. Construction of Cba. limnaeum bciD gene inactivated mutant.
(A) Schematic map of genes arrangement around bciD gene in the genome of Cba. limnaeum RK-j-1, and its insertional inactivation. The aadA1 gene, conferring resistance to streptomycin and spectinomycin, was inserted in bciD. Arrows represent the primers bciD-F (i), bciD-R (ii), bciD-inf-F (iii), bciD-inf-R (iv), bciD-comf-F (v), and bciD-comf-R (vi). (B) PCR confirmation of gene interruption. The bciD gene was amplified from genomic DNA extracted from the wild type (lanes 1 and 2) and a mutant (lanes 3 and 4) of Cba. limnaeum, using above bciD-comf-F and -R primers. The products in lanes 2 and 4 were then digested by restriction enzyme EcoRV, and the fragments yielded from wild type and the mutant were 1.36 and 0.78, and 2.22 kbp, respectively. Lane M, molecular size marker (the sizes of bands are indicated at left).