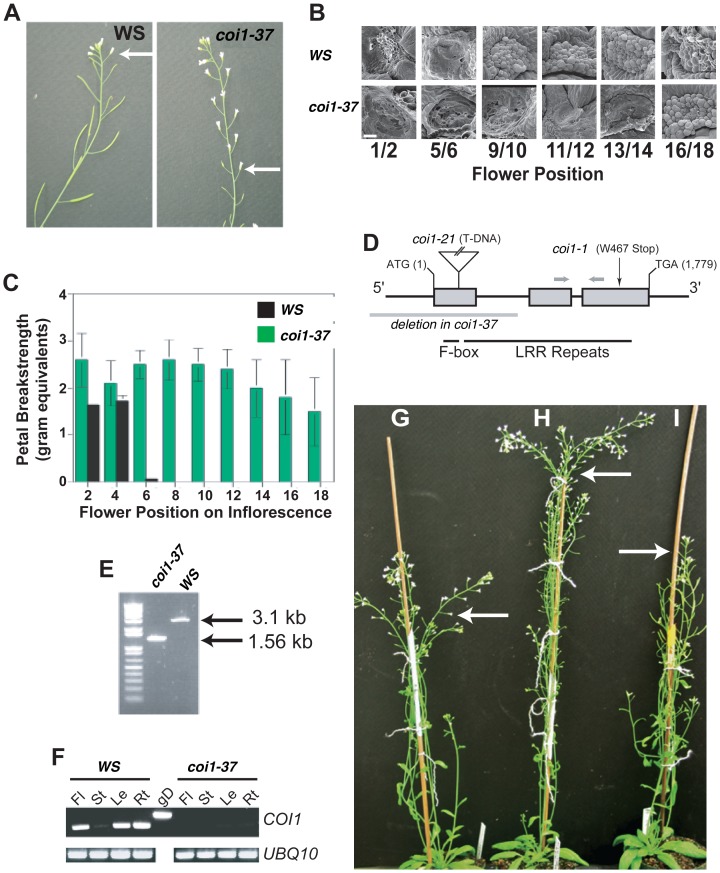
Figure 1. Isolation and Phenotypic, Molecular and Genetic Analysis of Novel dab Mutants.
(A) Close-up of WS and dab4-1 (coi1-37) inflorescences. Arrows indicate the flower position 7 in WS and 16 in dab4-1 (coi1-37). (B) Revealed fracture planes of the petal abscission zones were examined using scanning electron microscopy. Images were taken after petals were forcibly removed for each position. Flower positions as indicated are shown. Scale bar, 10 µm. (C) The force to remove a petal from each flower position was measured in dab4-1 (coi1-37) and WS. (D) Diagram showing location of mutations for coi1-37, coi1-21 and coi1-1. Primer locations for RT-PCR are denoted with arrows. (E) 1,537 bp deletion in coi1-37 was examined using PCR and confirmed by sequencing the amplicons from both coi1-37 and WS. (F) Expression of DAB4/COI1 was examined in Fl (Flower), St (Stem), Lf (Leaf), and Rt (root) using RT-PCR. gD denotes genomic DNA amplicon using the same primer set. UBQ10 was used as a loading control. (G-I) Genetic complementation of coi1-37 with coi1-21 and coi1-1. coi1-21-/- and coi1-1−/− were crossed to dacoi1-37+/−. Test cross analysis was performed to examine the delayed floral organ abscission phenotype was examined in the test cross population of (G) coi1-21−/− x coi1-37+/− and (H) coi1-37−/− x coi1-17+/− compared to WS (I).