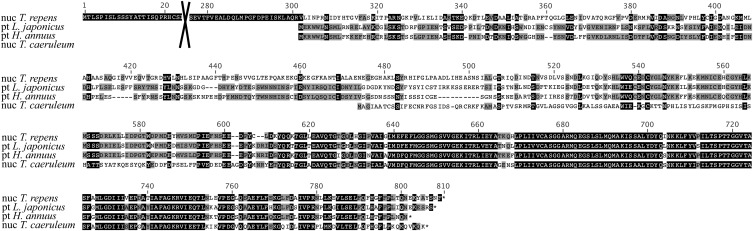
Figure 7.
T. caeruleum and T. repens n-accD protein sequences only present similarity for plastid derived sequences. Multiple alignment of n-accD predicted protein sequences from T. repens (Fabaceae) and T. caeruleum (Asterales) with the pt-accD protein sequences from Lathyrus japonicus (Fabaceae) and H. annuus (Asterales). Sequence conservation between all four peptides is restricted to the carboxy terminus corresponding to the carboxylase domain of the plastidic protein. Amino acids 24-275 encoded by the n-accD transcript of T. repens are not shown.