Figure 6.
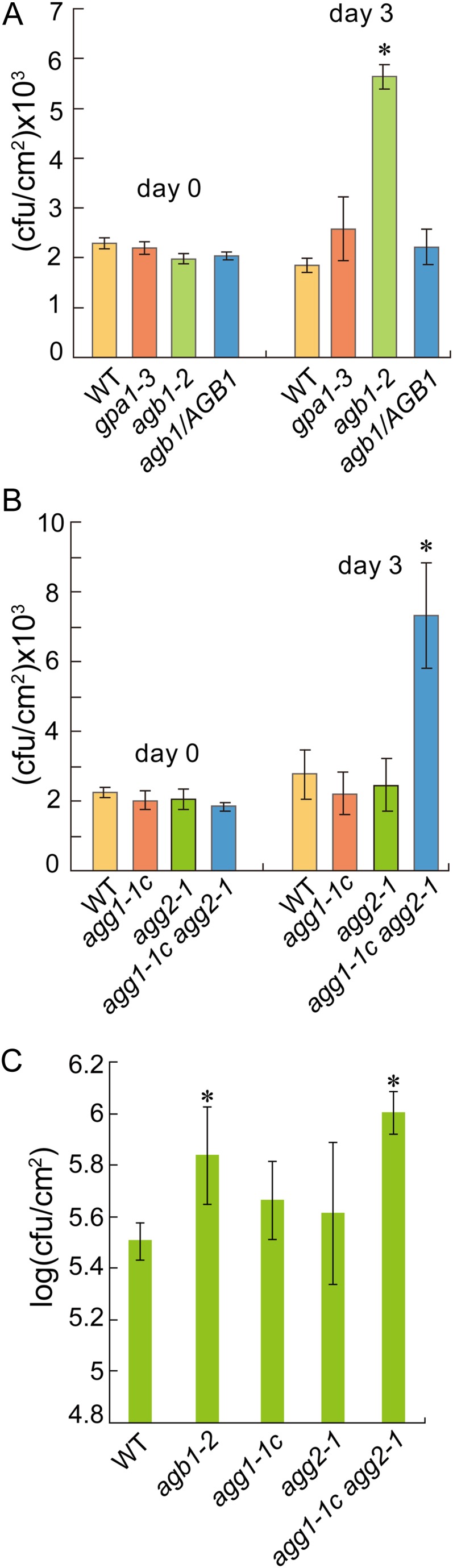
Growth of P. syringae pv tomato DC3000 hrcC and P. syringae pv tomato DC3118 in heterotrimeric G-protein mutants. A, Growth of P. syringae pv tomato DC3000 hrcC in the wild type, gpa1-3, agb1-2, and agb1-2 expressing a wild-type AGB1 transgene (agb1/AGB1). Asterisks above the bars indicate significant difference from the wild type (*P < 0.01). B, Growth of P. syringae pv tomato DC3000 hrcC in the wild type, agg1-1c, agg2-1, and agg1-1c agg2-1. Leaves of 6-week-old plants grown under short-day conditions (10-h day/14-h night cycles) were infiltrated with P. syringae pv tomato DC3000 hrcC (OD600 = 0.002). Bacterial titers at days 0 and 3 were measured by taking leaf discs within the inoculated area. Error bars represent sds from means of six samples. Asterisks above the bars indicate significant difference from the wild type (*P < 0.01). C, Growth of P. syringae pv tomato DC3118 in the wild type, agb1-2, agg1-1c, agg2-1, and agg1-1c agg2-1. Five-week-old plants were inoculated by spraying with a bacterial suspension at OD600 = 0.2. Samples were collected 3 d post inoculation to determine the bacterial titers. Asterisks above the bars indicate significant difference from the wild type (*P < 0.01). WT, Wild type. [See online article for color version of this figure.]
