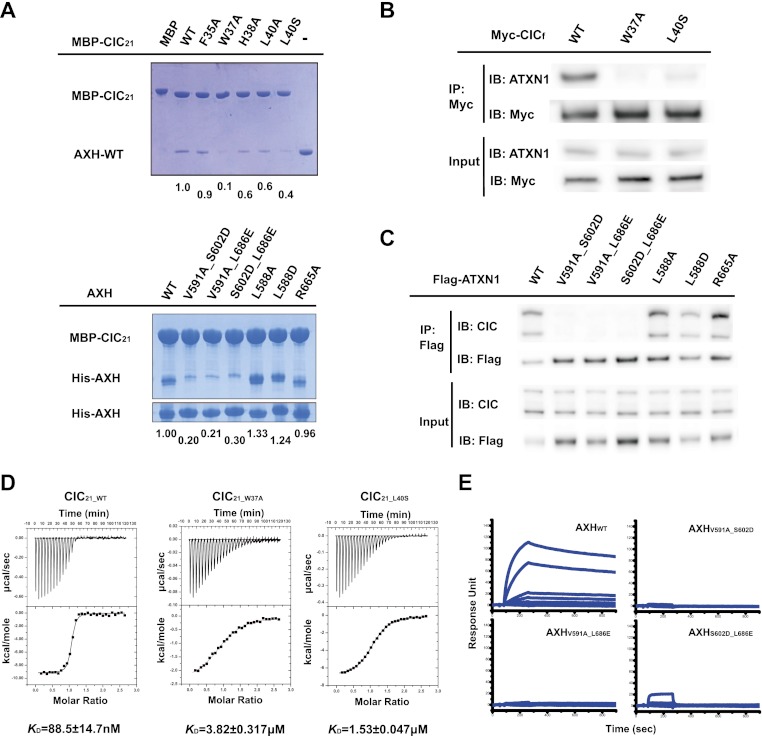
Figure 2.
Mutation in critical residues disrupts the interaction between the ATXN1 and CIC both in vitro and in vivo. (A, top) MBP pull-down assay with wild-type and mutant MBP-CIC21 and the wild-type AXH domain. (Bottom) MBP pull-down assay with wild-type MBP-CIC21 and wild-type and mutant AXH domains. Mutations in MBP-CIC21 (W37A and L40S) and His-AXH (V591A_S602D, V591A_L686E, or S602D_L686E) greatly disrupt the interaction. The same amounts of the AXH domains used for MBP pull-down were shown by His pull-down for His-AXH domains. The amount of bound AXH domain is quantified at the bottom of the gels. (B) In vivo binding between endogenous ATXN1 and Myc-tagged full-length CIC (CICf). One-hundred nanograms of each CICf construct was used for transfection. (C) In vivo binding between endogenous CIC and full-length wild-type and mutant ATXN1 (R566A is a negative control). The upper band of CIC is the longer isoform (CIC-L), and the lower band is the short isoform (CIC-S). Fifty nanograms of each Flag-ATXN1 construct was used for transfection. (D) ITC measurements between the AXH domain and CIC21_WT, CIC21_W37A, and AXH-CIC21_L40S. CIC21_W37A and AXH-CIC21_L40S have greatly reduced affinity to the AXH domain compared with CIC21_WT. (E) SPR measurements of the binding affinities between CIC21 and the AXH domain. The KD for the binding between CIC21 and AXHWT is ∼40 nM.. AXHV591A_S602D, AXHV591A_L686E, and AXHS602D_L686E fail to bind to CIC21.