Figure 2.
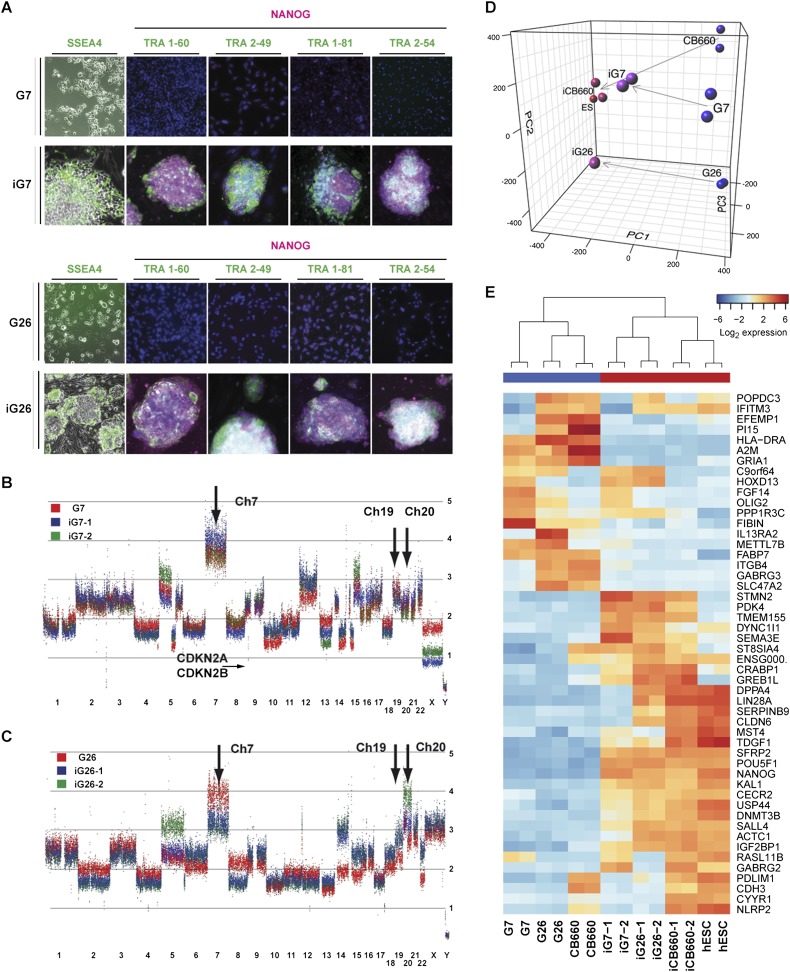
Gene expression profiling and marker analysis confirms that iG7 and iG26 are reprogrammed to a hESC/iPSC state. (A) Immunocytochemistry for pluripotency marker NANOG and cell surface markers (SSEA4, TRA1-60, TRA2-49, TRA1-81, and TRA2-54). All tested iG7 and iG26 clonal cell lines (iG7-1, iG7-2, iG7-3; iG26-1, iG26-2, and iG26-3; P4–P10) were immunopositive for these pluripotency markers (iG7-1 and iG26-1 are shown), whereas parental GNS lines G7 and G26 were negative. SSEA4 immunostaining is shown in live cells. (B,C) Genomic analysis using Affymetrix SNP 6.0 microarrays for GNS cells (red) and their reprogrammed derivatives (GiPSCs, P8–P12; blue and green) identifies many hallmark genetic changes common to GBM, such as amplification of chromosomes 7, 19, and 20 (arrows) and losses of chromosomes 13, 14, and 15. G7 and iG7 also display a 400-kb deletion that includes CDKN2A and CDKN2B (small arrow). (D,E) PCA of global gene expression (D; see also Supplemental Fig. 2A) and hierarchical clustering (E) of the 50 most significantly differentially expressed genes for normal NS cells and GNS cells (CB660, G7, and G26), hESCs and two clonal GiPSCs (iG7-1, iG7-2; iG26-1, and iG26-2), and iPSCs (iCB660) confirms that iG7 and iG26 are extensively reprogrammed to an ESC-like state. Analyzed iPSCs and GiPSCs were between passages 6 and 11.