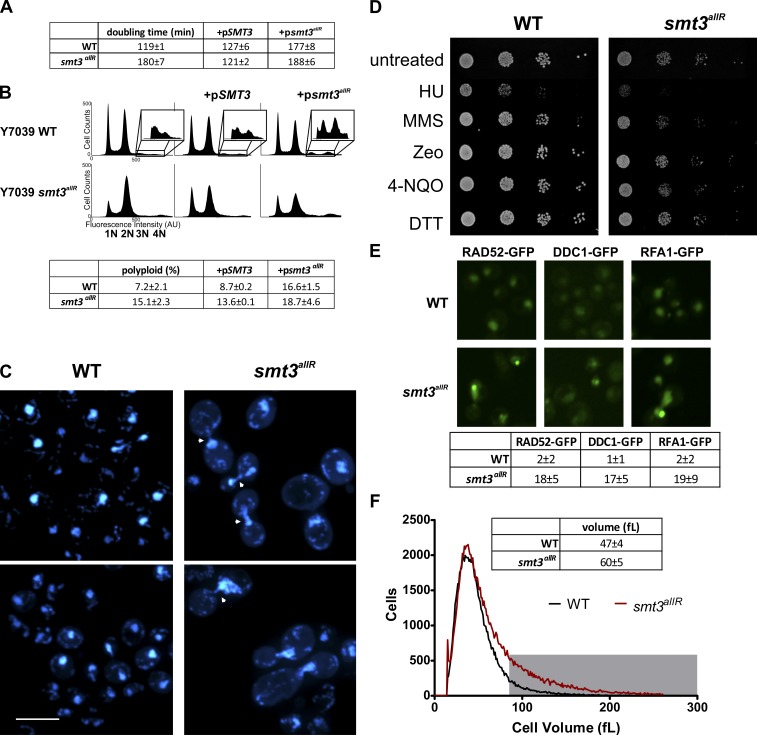
Figure 2.
smt3allR mutant yeast strains display increased doubling time, chromosome segregation defects, and increased ploidy, and are sensitive to DNA replication inhibitors. (A) Doubling time (mean ± SD) was measured over an 8-h period of log-phase growth for smt3allR and parental strains. Strains (as indicated) were also transfected with a galactose-inducible SMT3 (WT) or smt3allR plasmid (+pSMT3 or +psmt3allR, respectively), which was induced for 18 h before the first doubling time measurement. (B) FACS analysis of untransfected parental and smt3allR strains, and the same strains expressing the WT or allR SUMO proteins (as in A). DNA was stained with SYTOX green and data were collected on 50,000 events. The insets highlight the polyploid (>2n) population in each analysis. (C) Parental and smt3allR strains were stained with DAPI and imaged using confocal microscopy. Two representative images from each strain are shown. Cells displaying abnormal chromosome segregation are highlighted with arrowheads. Bar, 10 µm. (D) Log-phase cells were treated as indicated for 1 h, serially diluted (10×), and spotted onto YPD plates (HU, hydroxyurea; MMS, methyl methanesulfonate; Zeo, zeocin; 4-NQO, 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide; DTT, dithiothreitol; Linger and Tyler, 2005; Rand and Grant, 2006; Tang et al., 2009). Colonies were grown for 2 d at 30°C. (E) Spontaneous DNA damage foci were quantified in parental and smt3allR strains using GFP-tagged RAD52, DDC1, and RFA1. The mean number of foci (±SD) from four fields is tabulated. Bar, 10 µm. (F) Cell size distribution (mean ± SD) was measured on a Z2 counter (Beckman Coulter), as in Jorgensen et al. (2002). The gray box highlights the cell population with a volume >80 fL in the parental (black line) and smt3allR (red line) strains. Data shown are from a single representative experiment, conducted twice.