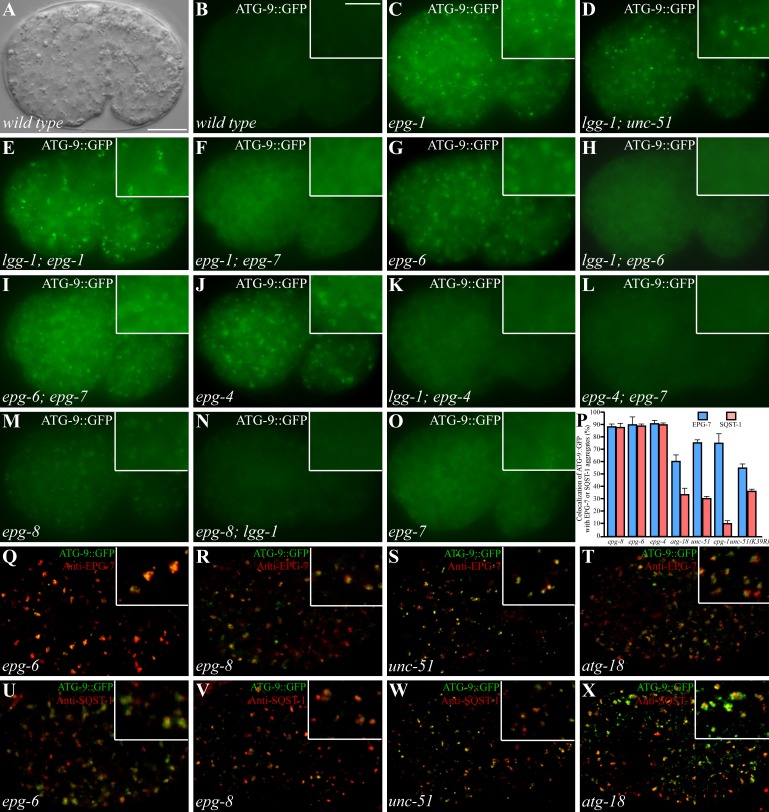
Figure 6.
Formation of ATG-9 puncta in various autophagy mutants. (A and B) In wild-type embryos, ATG-9::GFP is diffusely localized in the cytoplasm. (A) DIC image of the embryo shown in B. Insets show a magnified view. (C) ATG-9::GFP forms a large number of small, intense puncta in epg-1 mutants. (D and E) Accumulation of ATG-9::GFP puncta in unc-51(D) and epg-1 (E) mutants is independent of lgg-1. (F) The ATG-9::GFP puncta largely disappear in epg-1;epg-7 mutants. (G) ATG-9::GFP accumulates into large punctate structures in epg-6 mutants. (H) Loss of function of lgg-1 suppresses the accumulation of ATG-9::GFP puncta in epg-6 mutants. (I) Loss of function of epg-7 has no effect on the formation of ATG-9::GFP puncta in epg-6 mutants. The ATG-9::GFP puncta are smaller in epg-6;epg-7 mutants than those in epg-6 single mutants. (J–L) ATG-9::GFP accumulates into large punctate structures in epg-4 mutants (J) and the accumulation is suppressed by simultaneously depleting the activity of lgg-1 (K) or epg-7 (L). (M and N) In epg-8 mutants, ATG-9 accumulates into aggregates (M) that are suppressed by loss of lgg-1 activity (N). (O) epg-7 mutants exhibit the same distribution pattern of ATG-9::GFP as wild-type embryos. (P) Percentage of ATG-9::GFP puncta colocalized with EPG-7 and SQST-1 aggregates in indicated autophagy mutants. (Q–T) The ATG-9::GFP puncta in epg-6 (Q), epg-8 (R), unc-51 (S), and atg-18 (T) mutants colocalize with EPG-7 aggregates. (U and V) ATG-9::GFP puncta in epg-6 (U) and epg-8 (V) mutants colocalize with SQST-1 aggregates. (W and X) In unc-51 (W) and atg-18 (X) mutants, ATG-9::GFP partially colocalizes with SQST-1 aggregates. Bars: (A–O and Q–X) 10 µm; (insets in B–O and Q–X) 5 µm.