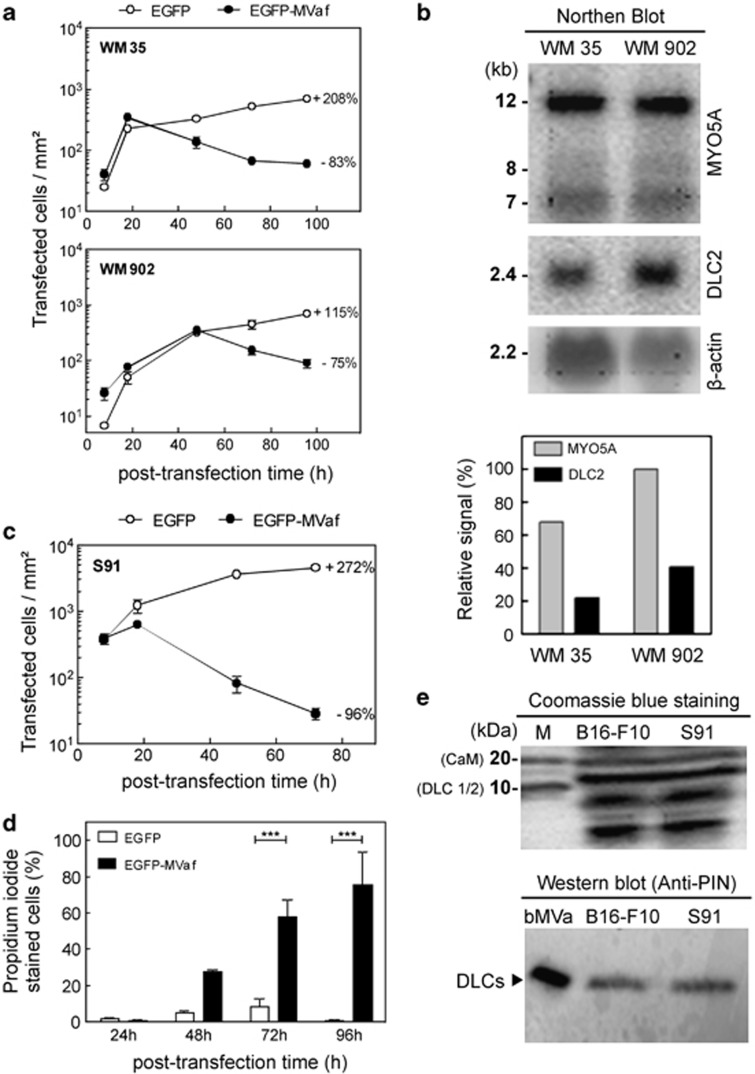
Figure 4.
Human melanoma cell lines are prone to cell death triggered by MVaf1 and levels of myosin-Va/DLC2 appears to influence cell death sensitivity. (a). Proliferation rates of WM35 and WM902 cells expressing either EGFP (control) or EGFP-MVaf1 were determined as the average number of fluorescent cells per area of growth (20 random fields of 1.6 mm2 per dish; n=4), after 8, 18, 48, 72 and 96 h of transfection. Rates are expressed as a percentage increase or decrease in culture proliferation from 18–96 h (WM35) or 48–96 h (WM902) post transfection (on the right-hand side of proliferation curves). (b) Northern blot analysis. MYO5A and DLC2 gene expression profiles in human melanoma cell lines WM35 and WM902. Densitometry of the specific bands was done measured by the ratio of pixel intensity (relative signal) using ImageJ gel analysis software; β-actin mRNA was used as the loading control. (c) Proliferation rate of Cloudman S91 mouse melanoma cells (bearing a MYO5A loss-of-function mutation) expressing either EGFP (control) or EGFP-MVaf1. Rates expressed as percentage increase or decrease in proliferation from 18 to 72 h post transfection are indicated. (d) Cell death rates for Cloudman S91 cells expressing EGFP-MVaf1 and EGFP were determined by PI staining at 24, 48, 72 and 96 h post transfection. After imaging 20 random fields per dish (n=5), the percentage of unviable cells was calculated relative to the total number of green fluorescent cells. (e) Detection of DLCs in B16-F10 and S91 cell lysates. Cell lysates from B16-F10 and Cloudman S91 were collected, equivalent amounts of total protein was loaded and analyzed by electrophoresis on a 5–20% SDS-PAGE, stained with Coomassie blue (top panel). Anti-DLC/PIN, which recognizes both DLC 1 and 2, was used as detection antibody (bottom panel). bMVa, purified fraction of native myosin-Va from chick brain, was used as positive control for the detection of the light chain DLC2 (as indicated)