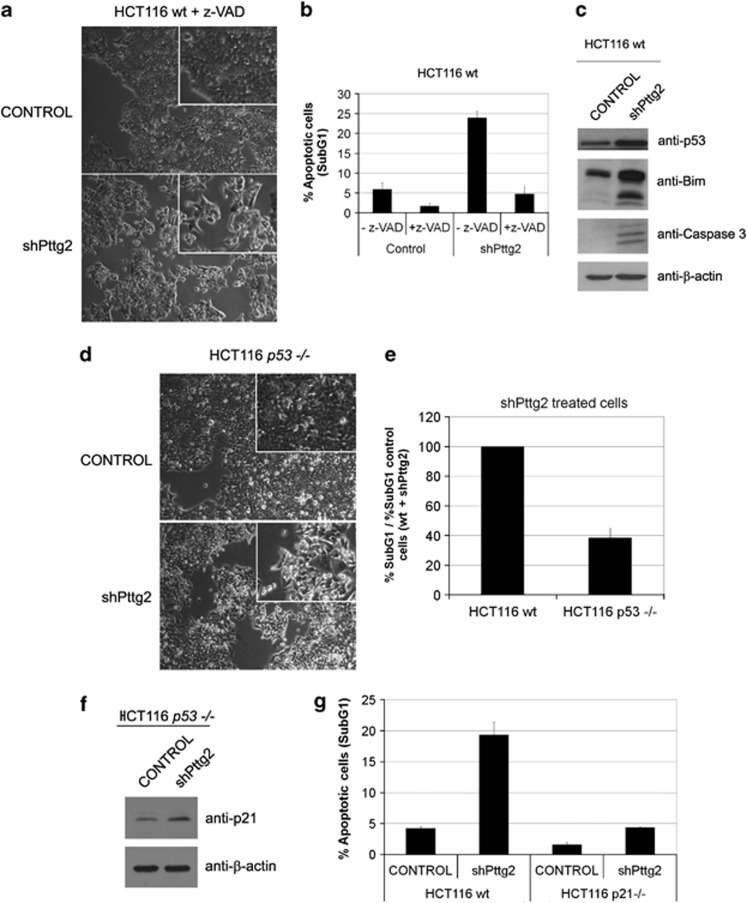
Figure 4.
Defective adhesion in Pttg2-depleted HCT116 cells results in p53- and p21-dependent apoptosis. (a) Phase-contrast images of Pttg2-silenced HCT116 cells after z-VAD treatment. A round morphology was still observed in Pttg2-depleted cells, suggesting a defective cell adhesion. (b) Apoptosis can be rescued in Pttg2-silenced HCT116 cells after caspase inhibition treatment. The percentage of apoptotic cells (subG1) after PTTG2 depletion was drastically reduced after treatment with the caspase inhibitor z-VAD. Bars represent the mean±S.E.M. (c) Levels of apoptotic indicators in Pttg2-silenced HCT116 cells. Cells were harvested after 72 h post-infection and assayed for p53, p21, BIM and cleaved-Capase 3 levels by western blot using specific antibodies. β-Actin was used as loading control. (d, e) Role of p53 in Pttg2-dependent anoikis. (d) Phase-contrast images of Pttg2-depleted HCT116 p53−/− cells. The absence of PTTG2 in HCT116 p53−/− results in cell rounding similar to wild-type HCT116 cells. (e) FACS analysis of Pttg2-depleted HCT116 p53−/− cells. In the absence of PTTG2, the percentage of apoptotic cells (subG1) was partially reduced in HCT116 p53−/− cells compared with HCT116 wild-type cells. Bars represent the mean±S.E.M. (f) The induction of p21 in Pttg2-treated cells occurs in a p53-dependent manner. Western blot analysis of p21 levels in HCT116 p53−/− cells 72 h post-infection with shPttg2 or control lentivirus. β-Actin was used as loading control. (g) Role of p21 in anoikis in Pttg2-depleted cells. The percentage of apoptotic cells in HCT116 p21−/− following treatment with shPttg2 was significantly reduced compared with HCT116 wild-type cells. Bars represent the mean±S.E.M.