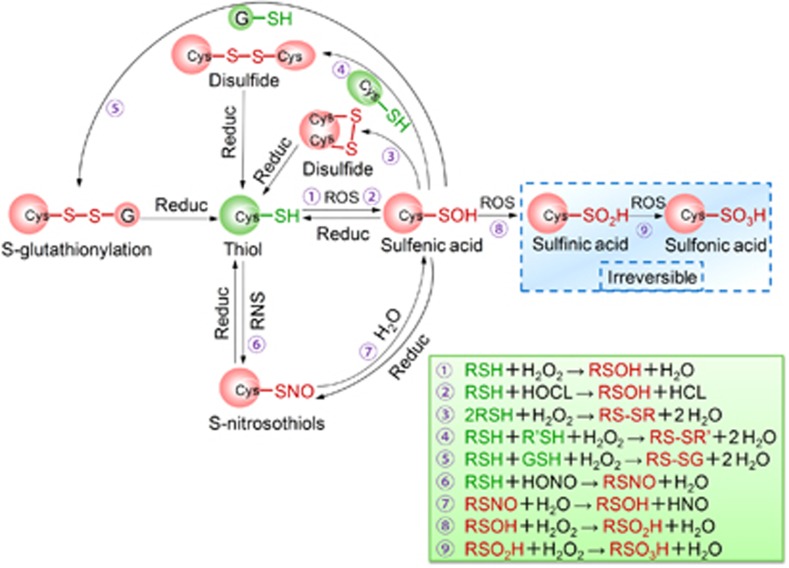
Figure 4.
Oxidative thiol modifications in redox-sensitive cysteine residues. Active thiol groups are easily oxidized to sulfenic acids (RSOH), the initial oxidation product. These transient sulfenic acids can also result from the hydrolysis of S-nitrosothiols (RSNO), which are the oxidative products of thiol groups in response to RNS. Sulfenic acids often condense with nearby thiols to form intermolecular or intramolecular disulfide bonds (RS-SR' or RS-SR), or with GSH resulting in S-glutathionylation (RS-SG). These oxoforms are reversible and can be restored to free thiols through the action of cellular reductants. Alternatively, sulfenic acids can be further oxidized to sulfinic acids (RSO2H) and, under more severe oxidizing conditions, to sulfonic acids (RSO3H), both of which are irreversible modifications. Cys, cysteine; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; GSH, reduced glutathione; Reduc, Reductants