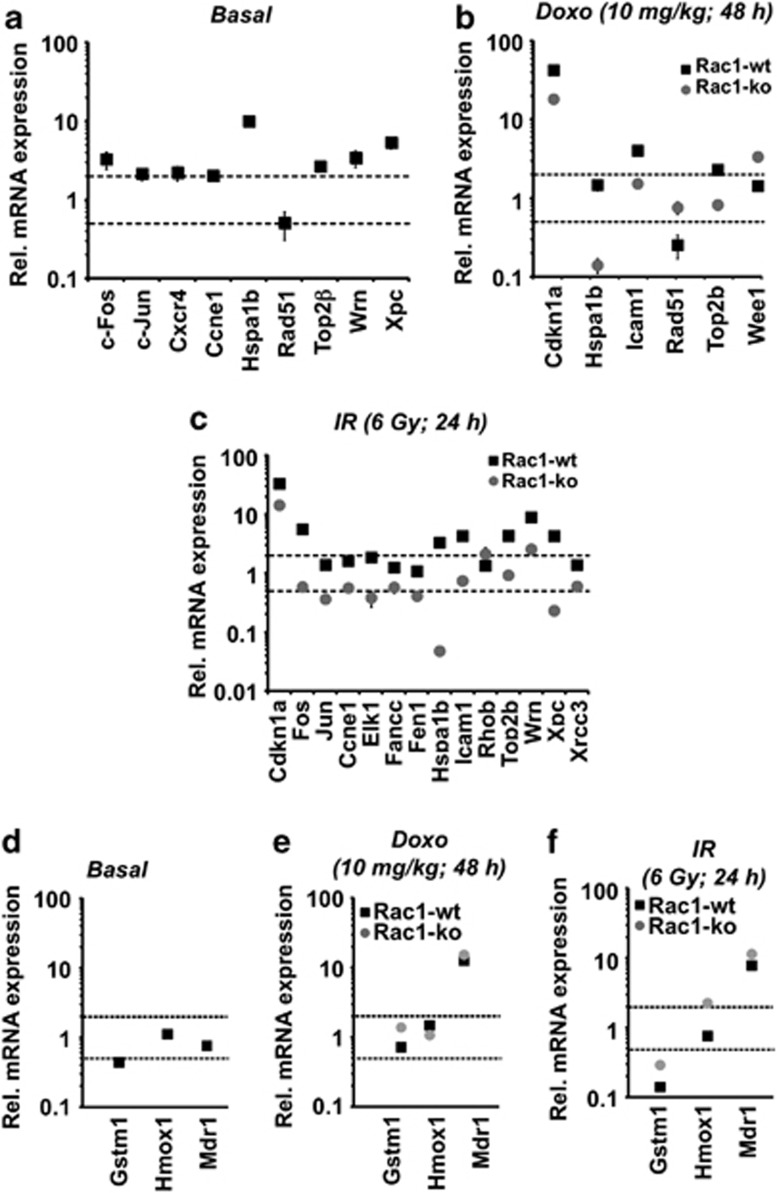
Figure 3.
Loss of Rac1 modulates acute changes in gene expression induced by genotoxin exposure. Rac1flox/flox/Mx1-Cre mice were left untreated or were treated with poly(I:C) (3 × 0.5 mg) every other day. Three weeks later, control mice that harbor the rac1 gene (Rac1-wt) or mice deleted for rac1 (Rac1-ko) were either left untreated (a), were treated with 10 mg/kg doxorubicin (Doxo) and were sacrificed 48 h later (b) or were irradiated with 6 Gy (TBI) (IR) and sacrificed 24 h later (c) for qRT-PCR-based analysis of hepatic mRNA expression as described in Materials and Methods. For normalization mRNA levels of GAPDH and β-actin were used. Differences in gene expression of ≤0.5-fold or ≥2-fold (indicated with the dotted lines) between treated and non-treated groups were considered as relevant. Differences in gene expression of >50% between Rac1-wt and Rac1-ko animals were also considered as relevant. Data shown are the mean±S.D. from triplicate determinations using cDNA synthesized from pooled RNA samples of n=3–4 mice per group. (a, d) Basal mRNA expression in the liver of rac1 knockout (Rac1-ko) animals was related to the expression in wild-type animals (Rac1-wt) which was set to 1.0. (b, c, e, f) Analysis of mRNA expression following genotoxin exposure was performed as described above. Relative mRNA levels in corresponding non-genotoxin-treated controls was set to 1.0