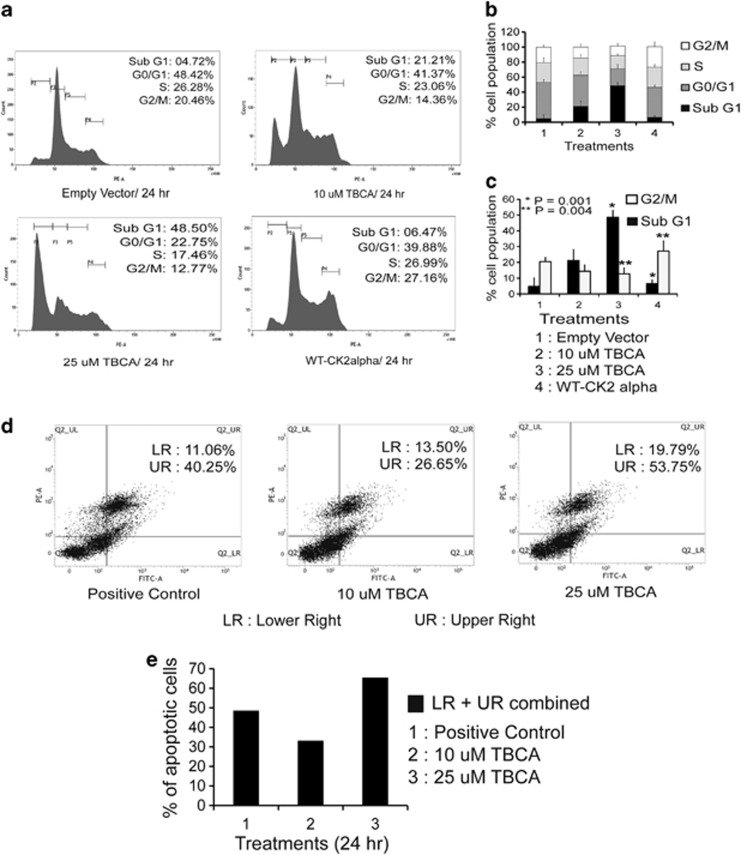
Figure 6.
Inhibition of CK2 significantly inflicts growth arrest followed by apoptosis of cancer cells. (a) PC3 cells were either treated with TBCA, or transfected with exogenous WT-CK2α. Cells were appropriately processed for cell-cycle analysis via FACS following transfection or treatment. (b) Comparative quantitation of cell percentage at the different phase of cell cycle. Cells were subjected to either treatment with TBCA or transfected with WT-CK2α. (c) Comparative quantitation, depicting percentage of cell population at sub-G0/G1 and G2/M phases of cell cycle upon treating the cells either with TBCA or overexpressing WT-CK2α by, with the respective level of significance (*P=0.004 and **P=0.009). (d) Inhibition of CK2 triggers apoptotic cell death. PC3 cells were treated with TBCA and appropriately processed for Annexin-PI labeling assay. Quadrate plot depicts the percentage of apoptotic cells. The lower right (LR) quadrant houses the early to early-mid apoptotic cells whereas the upper right (UR) quadrant represents cells chiefly at mid to mid-late apoptotic phases. In all, 25 μM of Camptothecin-treated cells served as positive control. (e) Comparative quantitation of total apoptotic cell population (both LR and UR) combined at the indicated concentrations of TBCA treatment for 24 h. In every case, bars represent (±) S.D. of three independent biological repeats at the mentioned level of significances. Control cells were transfected with appropriate empty vector where required, followed by DMSO-water treatment