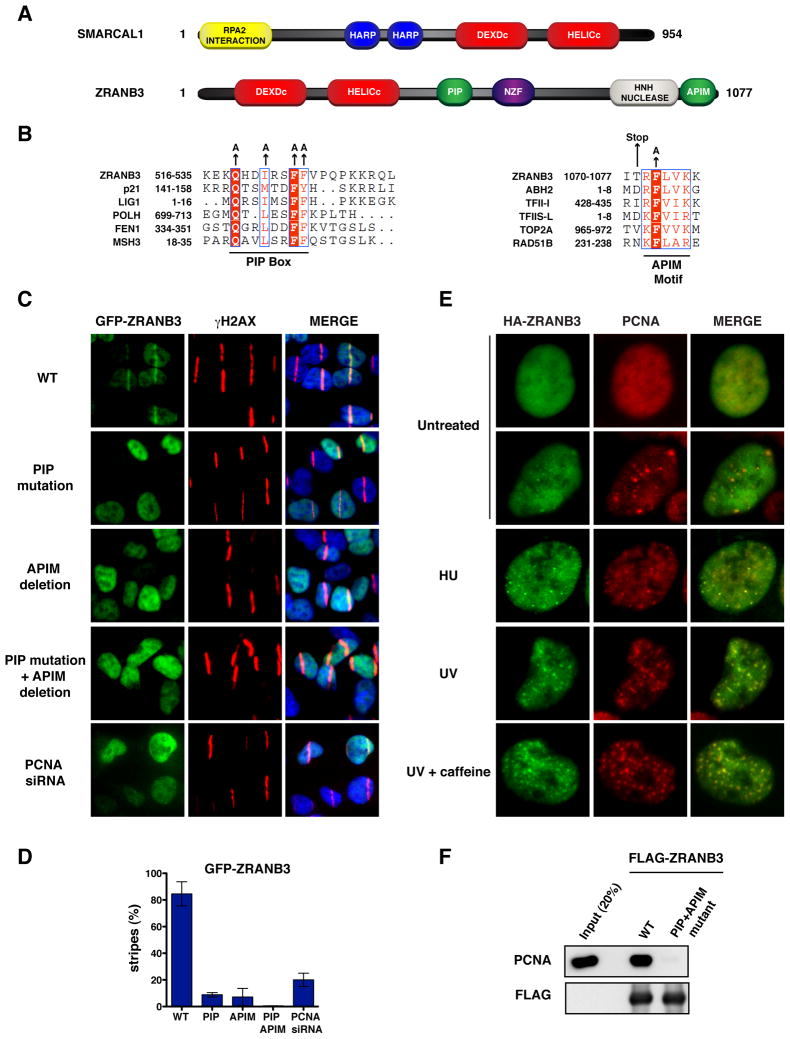
Figure 1. PCNA-dependent recruitment of ZRANB3 to DNA damage sites.
(A) Schematic representation of the protein domains of SMARCAL1 and ZRANB3. The helicase domains are indicated in red.
(B) Sequence alignments of the PIP box (left) and APIM (right) motifs of ZRANB3 with known PIP box and APIM motifs of other PCNA interacting proteins. The amino acids of the PIP box and APIM motifs that have been mutated are indicated by arrows.
(C) Localization of WT or mutant GFP-ZRANB3 to DNA damage sites generated by UV-laser microirradiation. U2OS cells expressing WT GFP-ZRANB3 are shown with or without PCNA siRNA treatment prior to UV microirradiation.
(D) Graphical representation of the percentage of U2OS cells that display co-localization of GFP-ZRANB3 with γH2AX at laser-generated stripes. The data represent the average and standard deviation of three independent experiments performed on cells expressing the GFP-constructs shown in (C).
(E) Co-localization of ZRANB3 with PCNA. U2OS cells expressing HA-ZRANB3 were left untreated or subjected to hydroxyurea (2 mM) or UV radiation (25 J/m2) treatment. Cells subjected to UV radiation were also treated with caffeine (2 mM). Cells were stained with anti-HA (green) and anti-PCNA (red) antibodies.
(F) Immunoprecipitation of FLAG-ZRANB3 with PCNA. FLAG-ZRANB3 either WT or mutated in the PIP and APIM motifs was purified from insect cells with anti-FLAG beads and then incubated with recombinant PCNA. Immunoprecipitated complexes were detected by western blotting.