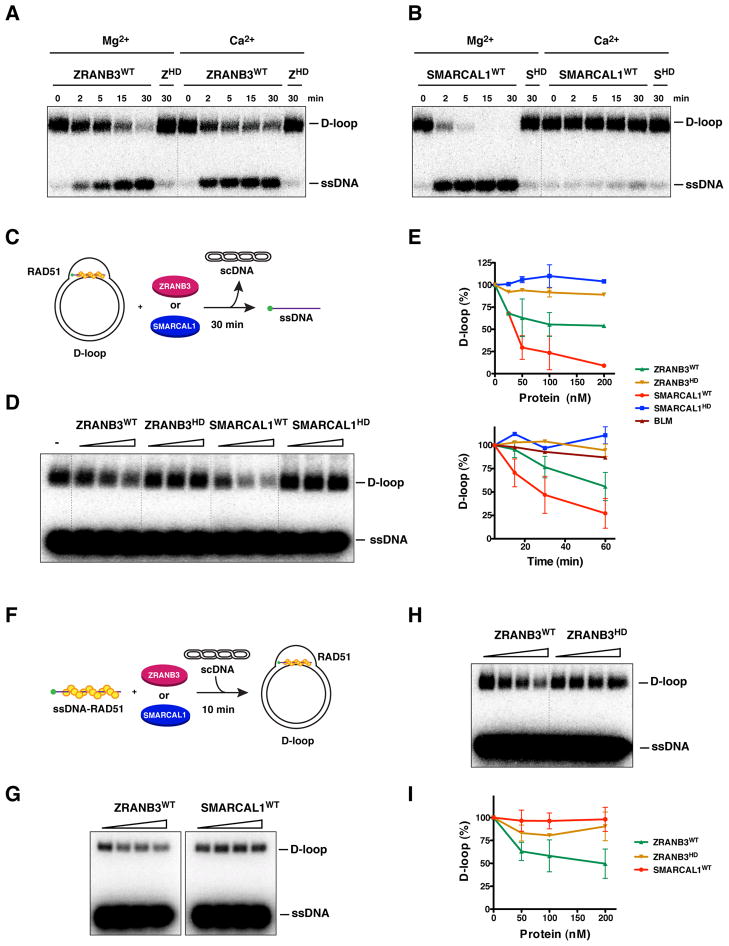
Figure 7. Disruption of D-loop structures by ZRANB3 and SMARCAL1.
(A) Dissociation of D-loops (400 nM) by ZRANB3, either WT or helicase-dead (HD) (100 nM) as a function of time. Experiments were performed in buffer containing either magnesium or calcium acetate (5 mM).
(B) D-loop structures generated as described in (A) were incubated in a time course reaction with either WT or helicase-dead (HD) SMARCAL1 (100 nM) in the presence of either magnesium or calcium acetate (5 mM).
(C) Schematics of the dissociation of preformed RAD51-containing D-loop structures by ZRANB3 and SMARCAL1.
(D) Increasing amounts of ZRANB3 and SMARCAL1 (25, 50 and 200 nM), either WT or mutant, were incubated with preformed RAD51-containing D-loops as depicted in (C).
(E) Quantification of the disruption of preformed RAD51-containing D-loop structures following addition of increasing (upper panel) or fixed amounts of ZRANB3 and SMARCAL1 proteins (100 nM) in a time course reaction (lower panel). The activity of BLM (100 nM) in the time course reaction is indicated. Points with error bars represent the average and standard deviation of three or more independent experiments.
(F) Schematics of the formation of RAD51-containing D-loop structures in the presence of ZRANB3 and SMARCAL1.
(G) Formation of RAD51-containing D-loop structures following addition of increasing amounts of ZRANB3 or SMARCAL1 proteins (50, 100 and 200 nM) as represented in the schematics in (F).
(H) Formation of RAD51-containing D-loop structures following addition of increasing amounts of either WT or mutant ZRANB3 (50, 100 and 200 nM).
(I) Quantification of the formation of RAD51-containing D-loops in the presence of ZRANB3 and SMARCAL1 proteins. Points with error bars represent the average and standard deviation of three or more independent experiments.