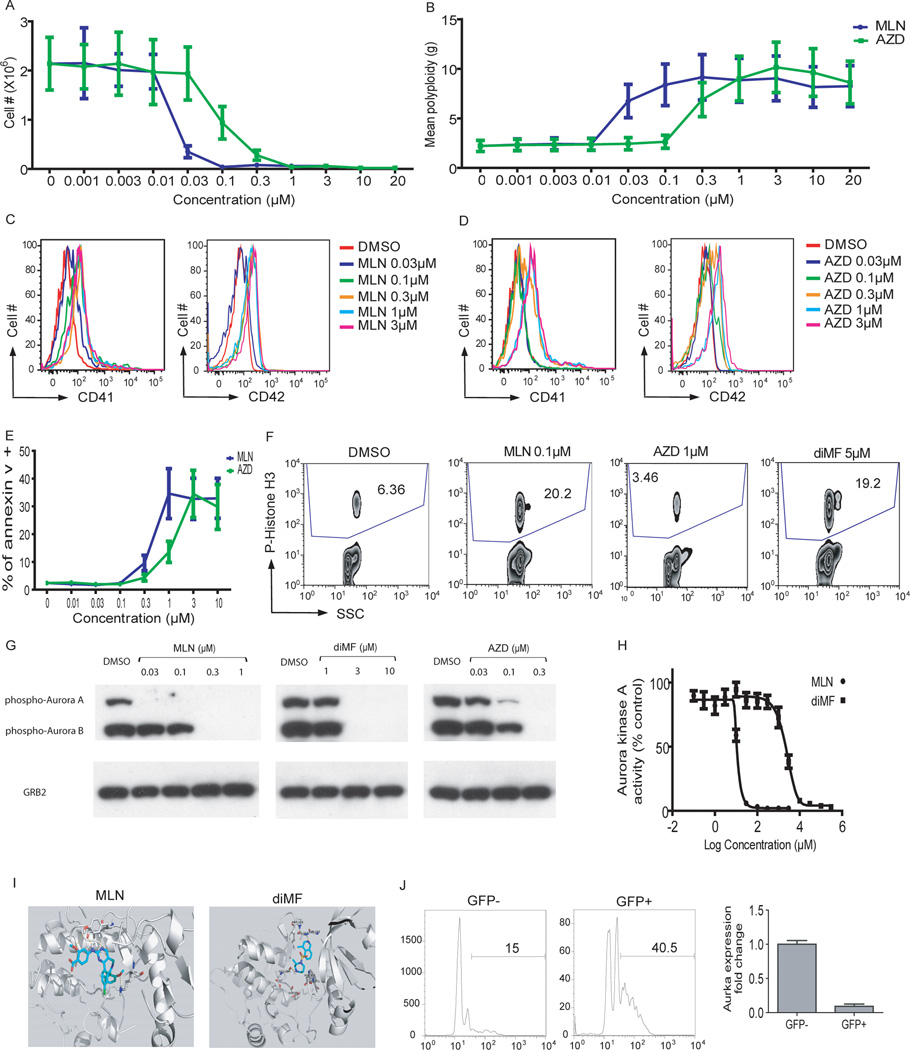
Figure 5. Inhibition of Aurora kinase A phenocopies diMF.
(A–E) MLN8237 and AZD1152-HQPA induced proliferation arrest (A), polyploidization (B), expression of CD41 and CD42 (C,D), and apoptosis (E) in CMK cells 72 hr after treatment. Data are representative of two experiments conducted in duplicate. Line graphs depict mean ± SD. (F) MLN8237 and diMF increased the phosphorylation of histone H3, while AZD1152-HQPA decreased its levels. (G) MLN8237, AZD1152-HQPA, and diMF differentially inhibited phosphorylation of Aurora kinases. CMK cells were incubated with 0.1 µM paclitaxel for 18 hr, then DMSO, MLN8237, AZD1152-HQPA, or diMF was added and incubated for 2 hr. The degree of phosphorylation of the Aurora kinases in each sample was determined by Western blot. Treatment of cells with 1 µM AZD1152-HQPA also led to complete loss of phospho-AURKA and AURKB (data not shown). (H) MLN8237 and diMF inhibit AURKA. Purified Aurora kinase A was incubated with MLN8237 or diMF and the change of AURKA phosphorylation was determined by spectrophotometry. Data are representative of two experiments conducted in triplicate. (I) Docking studies were performed to evaluate the binding of MLN8237 and diMF to Aurora kinase A using Schrodinger software. Both MLN8237 and diMF showed a strong hydrogen-bond network with the hinge residues of AURKA. (J) Excision of Aurka leads to enhanced polyploidization of megakaryocytes. Bone marrow cells from Aurkaflox/flox mice were transduced with MIGR1-Cre-IRES-GFP and the cells were cultured in the presence of THPO for 72 hours. (Left) The DNA contents of CD41+ cells from GFP+ (Cre-expressing) or GFP- (without Cre expression) populations of the same culture are shown. (Right) The levels of Aurka mRNA in sorted GFP-positive or GFP-negative cells were assayed by qRT-PCR. Data are representative of two experiments.