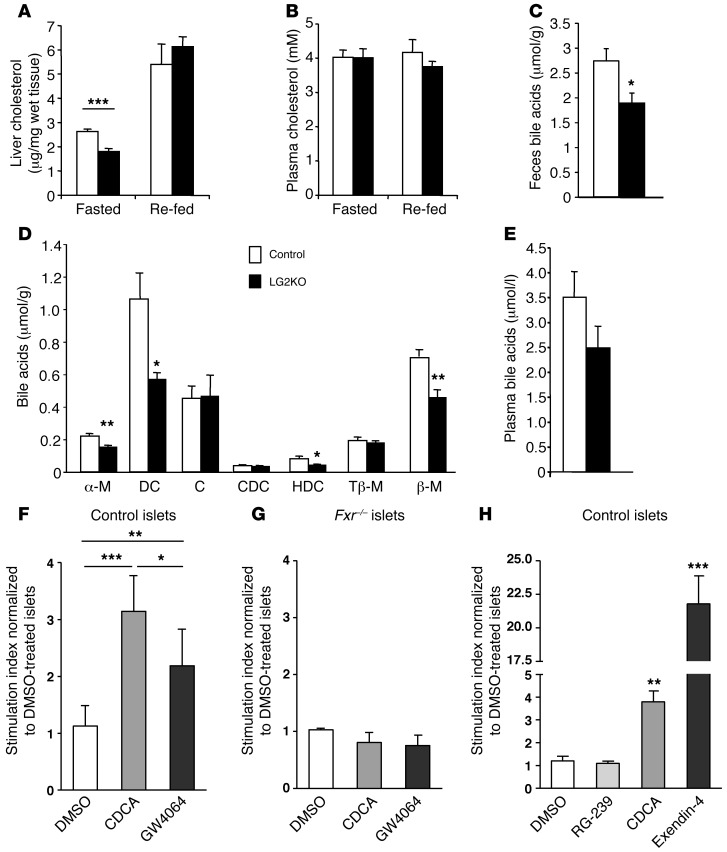
Figure 9. Reduced cholesterol and BA levels in LG2KO mice and potentiation of insulin secretion by BAs.
(A) Liver cholesterol content and (B) plasma cholesterol in fasted and re-fed control and LG2KO mice (n = 6). (C) BA content in feces of control and LG2KO mice collected over a 24-hour period (n = 7). (D) Composition of the fecal BAs: α-murocholic acid (α-M); deoxycholic acid (DC); cholic acid (C); chenodeoxycholic acid (CDC); hyodeoxycholic acid (HDC); tauro-β-murocholic acid (Tβ-M); and β-murocholic acid (β-M) (n = 7). (E) Total plasma BAs in the fasted state (n = 6). A–E: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; and ***P < 0.001 versus control. (F) Twenty-four-hour pretreatment of control islets with chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA, 50 μM), or the FXR agonist GW4064 (1 μM) increases glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. DMSO: vehicle. (G) No potentiation of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by FXR agonists in Fxr–/– islets. (H) One-hour glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by control islets performed in the presence of, and after a 48-hour treatment with, TGR5 (RG-239), FXR (CDCA), or GLP-1 receptor (exendin-4 [Ex4]) agonists. F–H: Pool of 5 different experiments. One-way ANOVA and post-hoc Tukey’s test: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; and ***P < 0.001. In H, statistical significance is calculated versus DMSO-treated islets.