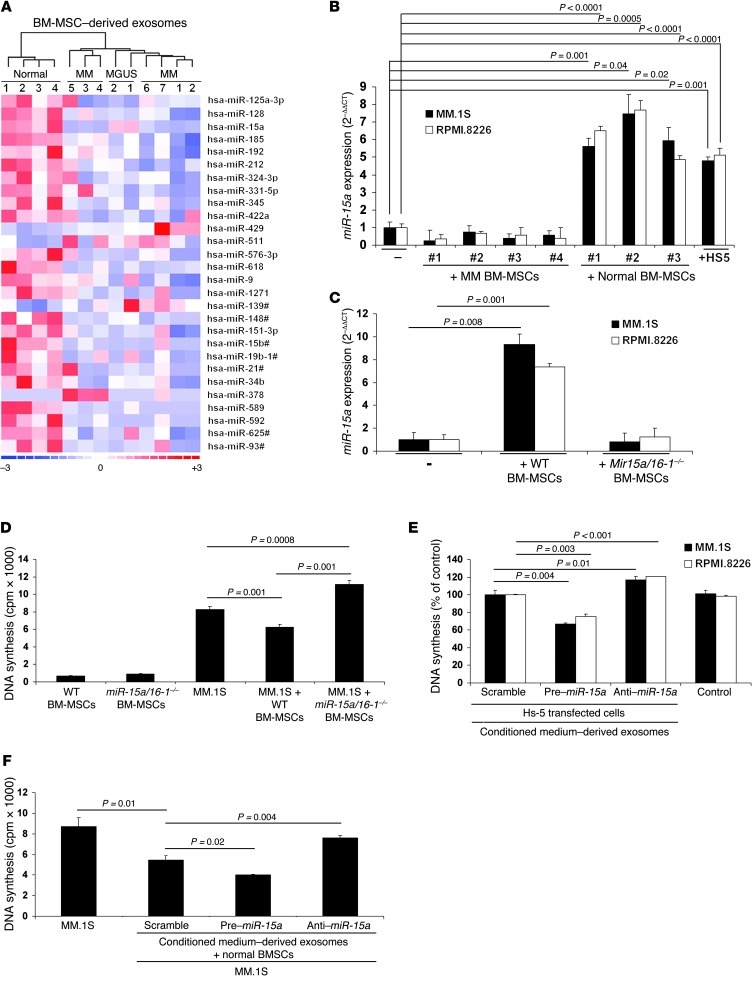
Figure 6. miR-15a expression differs between normal and MM BM-MSCs, and miR-15a–containing exosomes are transferred into MM cells.
(A) miR expression profiling on total RNA isolated from normal (n = 4), MM (n = 7), and MGUS (n = 2) BM-MSC–derived exosomes. A heatmap was generated after supervised hierarchical cluster analysis. Differential miR expression is shown by red (upregulation) versus blue (downregulation) intensity (d-Chip software; normal versus MM, 1.5-fold change, P < 0.05). (B) MM.1S and RPMI.8226 MM cells were cultured in the absence or presence of primary MM (n = 4) or normal (n = 3) BM-MSCs or the HS-5 cell line for 48 hours. miR-15a expression was determined by qRT-PCR in MM cells (2–ΔΔCt method, normalized to RNU6B miR as reference). Results are average ± SD of 3 independent experiments. miR-15a was upregulated in MM cells when in contact with normal BM-MSCs. (C) Murine exosomes were isolated from BM of WT or miR-15a/16-1–/– mice and subsequently added to MM cells for 48 hours. miR-15a levels were determined by qRT-PCR in human MM cells (2–ΔΔCt method, normalized to C. elegans miR-39 reference, used as spiked control). Bars represent SD. (D) MM cells were cultured in the presence or absence of murine WT or miR-15a/16-1–/– BM-MSCs for 48 hours, and cell proliferation was assessed as [3H]-thymidine uptake. Bars indicate SD. (E and F) HS-5 cells (E) or primary BM-MSCs (F) were transfected with scramble, pre–miR-15a, or anti–miR-15a probe. Cells were then exposed to the indicated exosomes for 48 hours. Cell-conditioned media absent cells and processed as in all samples tested served as control. Cell proliferation was assessed using [3H]-thymidine uptake assay. Bars indicate SD.