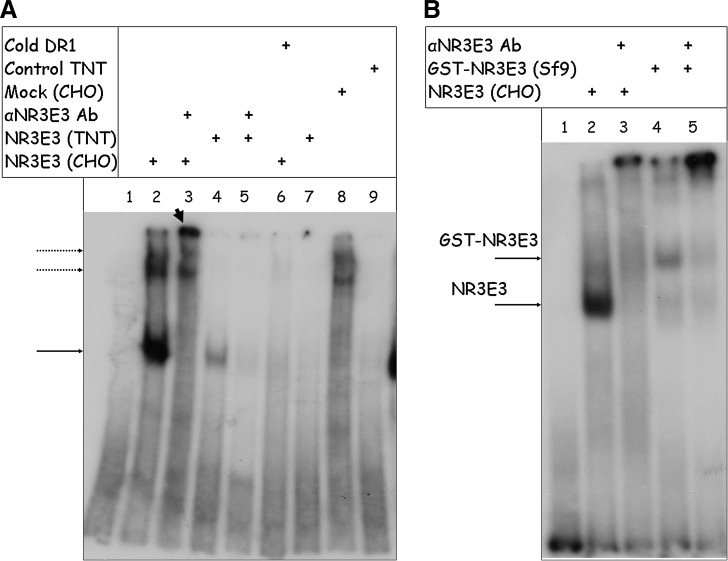
FIG. 2.
Characterization of protein NRE2E3 preparations in electrophoretic mobility-shift assay (EMSA). (A) EMSA analysis of CHO-cell-expressed and in vitro translated preparations of NR2E3. A cellular extract from CHO cells transfected with the NR2E3 vector was incubated with the 32P-labeled DR1-response element and electrophoresed on a nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel as described in the Methods section. Lane 1 contains the 32P-labeled DR1 element only. Lane 2 shows the DNA–protein complex formed by CHO-expressed NR2E3, whose specificity was confirmed by supershifting with the NR2E3-specific antibody (lane 3). Mock CHO cell extract was added in lane 8 for comparison with CHO-expressed NR2E3-DR1 complex. Lane 6 shows that binding of CHO-expressed NR2E3 to DR1 can be competed out by 50-fold molar excess of cold DR1. Lane 4 shows the weak DNA–protein band formed after mixing of DR1 with NR2E3 synthesized in the in vitro reticulocyte translation system, while lane 5 shows the effect of the specific NR2E3 antibody on this band. Reticulocyte lysate programmed with the control plasmid was added to DR1 in lane 9. Arrow indicates the position of a DR1-NR2E3 complex. Two dotted arrows indicate the position of nonspecific bands that are present in the mock CHO cell extract (lane 8) as well as in the NR2E3-expressing cell extract (lanes 2 and 3). Arrowhead (lane 3) points to the position of the NR2E3-DR1 complex supershifted with the specific antibody. Equal amounts of CHO-expressed and TnT-translated NR2E3 (as established by Western blotting) were used in this experiment. The longer run was required to assure adequate resolution of the DNA–protein complexes in a 6% nondenaturing DNA retardation gel that led to migration of labeled unbound DR1 out of the gel. (B) EMSA analysis of Sf9-expressed GST-NR2E3 purified using the FPLC system. Lane 2 shows the DNA–protein complex formed by CHO-expressed NR2E3, which can be supershifted with the NR2E3-specific antibody (lane 3). Lane 4 shows the weaker DNA–protein band formed after mixing of DR1 with GST-NR2E3 purified from Sf9 cells using FPLC, while lane 5 shows the effect of the specific NR2E3 antibody on this band. Arrows indicate the positions of DR1/NR2E3 and DR1/GST-NR2E3 complexes. NR2E3 immunoreactivity in CHO cells and purified GST-NR2E3 was compared using Western blotting, and volumes of CHO-expressed NR2E3 and purified GST-NR2E3 were adjusted, so equal amounts of NR2E3 were taken into the EMSA reaction.