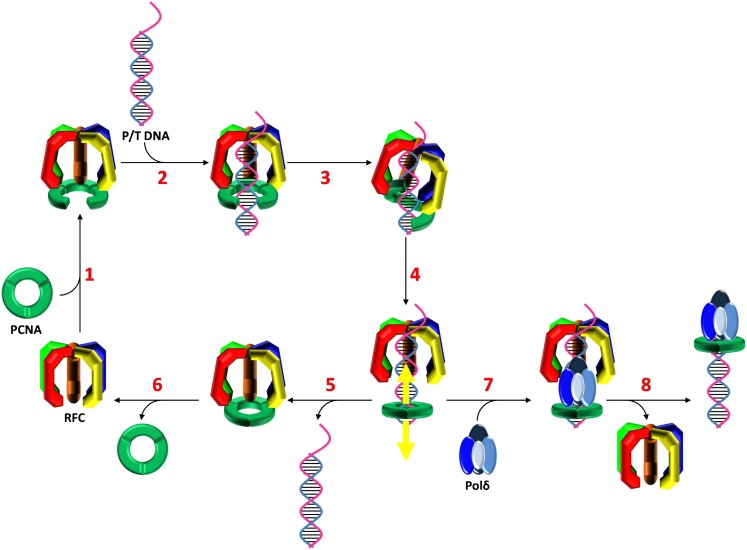
Figure 5. Stepwise assembly of the human DNA polymerase holoenzyme.
(1) RFC•ATP binds PCNA and opens it for assembly onto DNA. (2) The open PCNA•RFC•ATP complex binds to a P/T junction and (3) adopts the notched screw cap arrangement. (4) RFC hydrolyzes ATP, closing the PCNA ring and releasing it onto DNA. (5) In the absence of polymerase, loaded PCNA is unable to ‘escape' from DNA-bound RFC and is unloaded back into solution by RFC. (6) RFC subsequently releases PCNA, exchanges ADP for ATP, and the cycle repeats. (7) In the presence of polymerase, loaded PCNA is ‘captured' from DNA-bound RFC by an incoming polymerase, blocking the unloading activity of DNA-bound RFC by physical occlusion. (8) RFC subsequently dissociates, leaving behind the functional holoenzyme consisting of polymerase and PCNA.