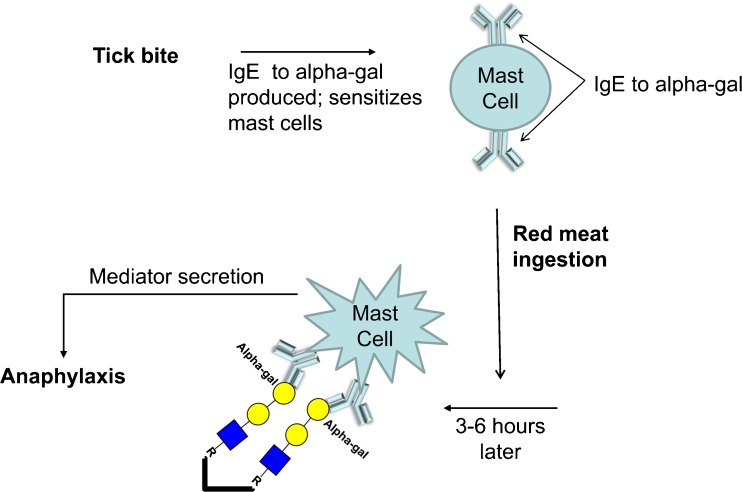
Figure 1.
Development of anaphylaxis to alpha-gal. Sensitization occurs after exposure to alpha-gal during tick bites. IgE to alpha-gal produced during sensitization binds to high affinity IgE receptors on mast cells and basophils, without causing symptoms. Re-exposure to alpha-gal in mammalian meat causes cross-linking of IgE:IgE receptor complexes on mast cells and basophils to induce secretion of various mediators that lead to anaphylaxis. (The oligosaccharide structures of the alpha-gal are shown in the symbolic depiction suggested by the Consortium of Functional Glycomics).