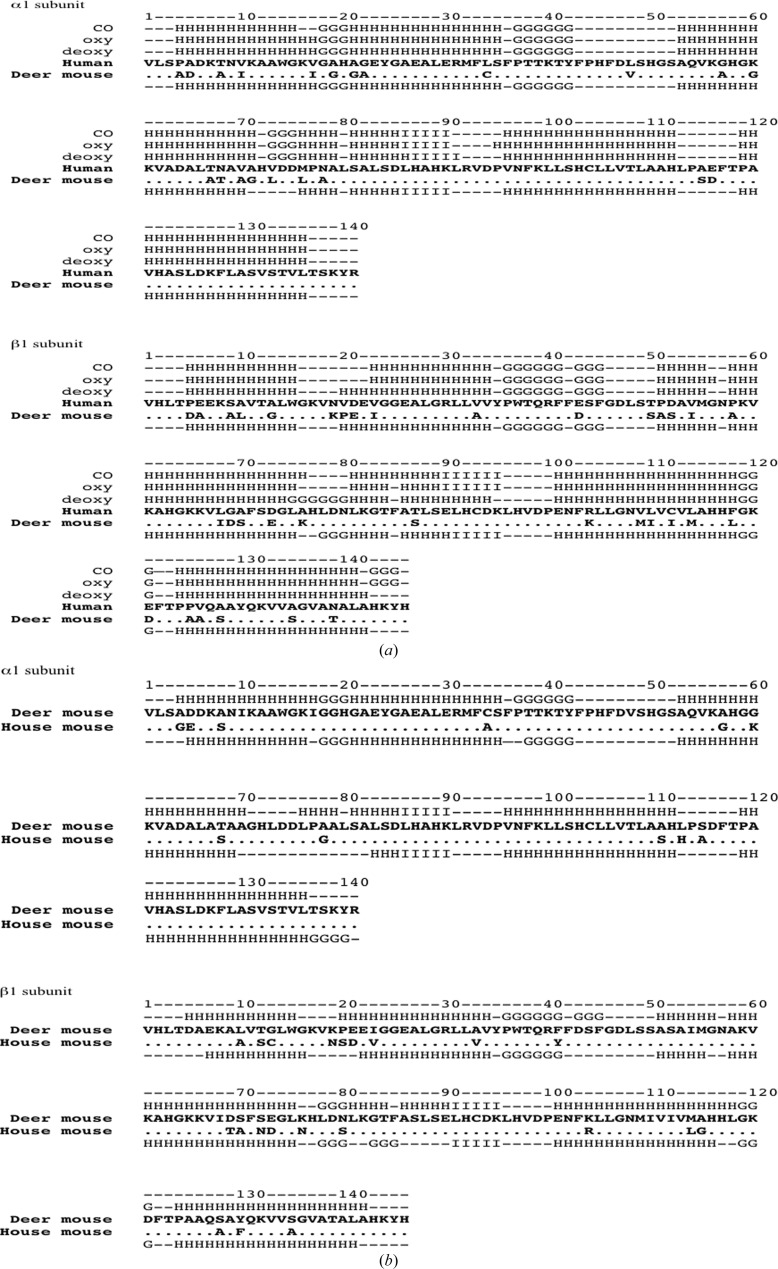
Figure 2.
Sequences and secondary-structure comparisons of deer mouse, house mouse and human hemoglobin. (a) Comparisons between deer mouse hemoglobin and three forms of human hemoglobin. Sequences of deer mouse and human hemoglobin α and β subunits were aligned separately; conserved amino-acid residues are denoted by dots. Secondary structures of three forms of human hemoglobin [the deoxy, oxy and carbonmonoxy (CO) forms] are presented above the human globin sequences and that of deer mouse hemoglobin is presented below the human sequence. H, α-helix; G, three-helix motif; I, five-helix motif; –, residues with no assigned secondary structure. (b) Comparisons between deer mouse hemoglobin and house mouse (Mus musculus) hemoglobin. The sequences of the α and β subunits of deer mouse and house mouse hemoglobin (PDB entry 3hrw) were aligned separately; identical amino-acid residues between the two species are represented as dots in the house mouse sequence. The secondary structure of deer mouse hemoglobin is presented above its sequence and that of house mouse hemoglobin is presented below its sequence.