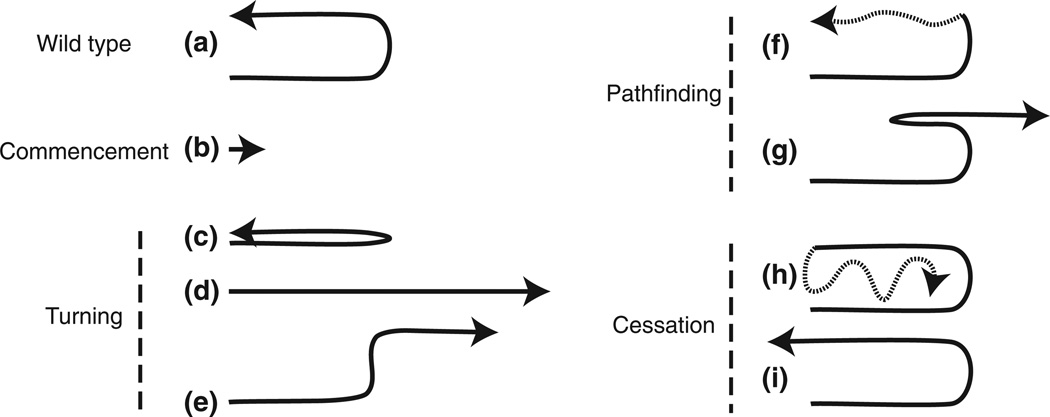
FIGURE 3.
Distal tip cell migration defects. Arrows show the direction of migration. Sections represented by dotted lines indicate potential variability in migration paths. A wild-type U-shaped migratory path is shown in (a). Defects are grouped according to the migration stages: commencement (b, no migration), turning (c, ventralized; d, no turn; e, wrong turn), pathfinding (f, meandering on dorsal; g, change in direction), and cessation (h, perpetual migration; i, overshoot). Only posterior gonads are represented, although these defects also occur in the anterior gonad arms.